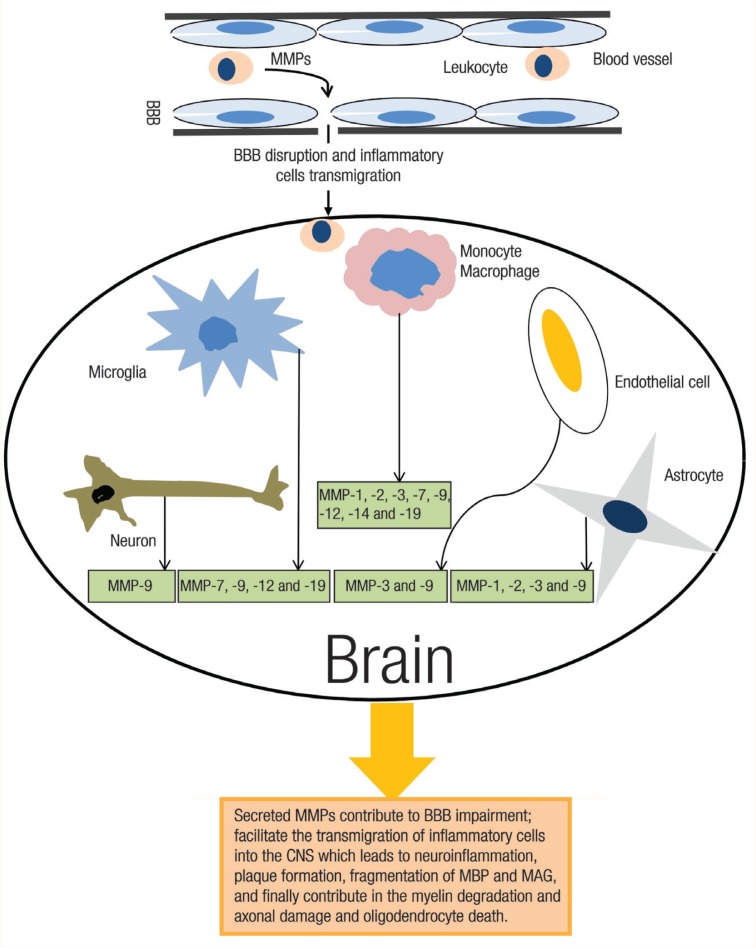
Figure 1:
In multiple sclerosis, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are expressed in the central nervous system (CNS) by various cell types, including vascular endothelial cells, neuron, reactive astrocytes and the microglia, and accumulated inflammatory cells. In the CNS, the high numbers of MMPs lead to the perpetuation of neuroinflammation, which contributes to myelin degradation and axonal damage.
BBB = blood-brain barrier; MBP = myelin basic protein; MAG = myelin-associated glycoprotein.