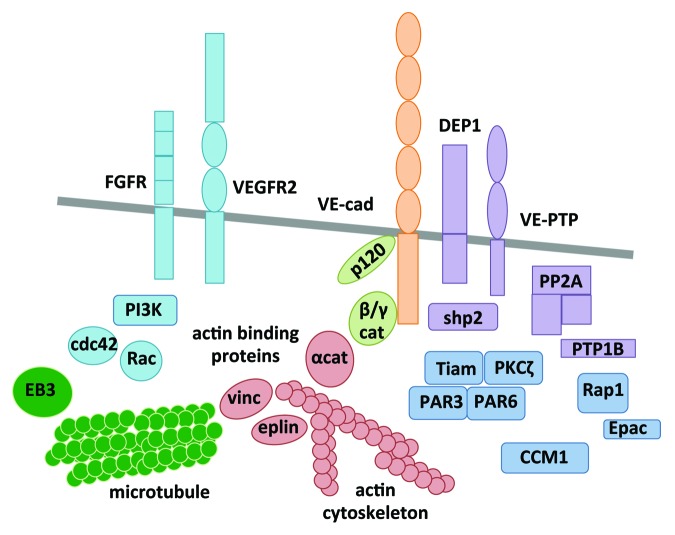
Figure 1. Assembly of VE-cadherin-mediated cell–cell contacts. Different classes of molecules interact with VE-cadherin (orange) and modulate its adhesive function: catenins (light green), actin binding proteins (red), phosphatases (purple), polarity complex (dark blue), signaling molecules and growth factor receptors (light blue), and microtubule (dark green). cat, catenin; cdc42, cell division control protein 42 homolog; CCM1, cerebral cavernous malformation protein 1; DEP1, density enhanced protein tyrosine phosphatase 1; EB3, end binding protein 3; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; PAR3/6, partition defect protein 3/6; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3 kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; PTP1B, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; Shp2, Src homology protein tyrosine phosphatase; Tiam, T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis; VE-cad, VE-cadherin; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; VE-PTP, vascular endothelial protein tyrosine phosphatase; vinc, vinculin.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.