FIGURE 1.
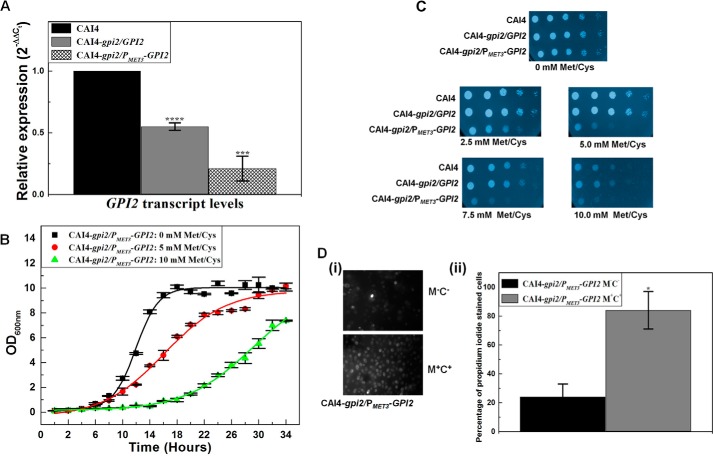
GPI2 affects growth and viability in C. albicans. A, GPI2 transcript levels were decreased by 1.8 ± 0.03-fold (****, p value = 0.000018) in GPI2 heterozygote (CAI4-gpi2/GPI2) and 4.8 ± 0.1-fold (****, p value = 0.00016) in conditional null GPI2 mutant (CAI4-gpi2/PMET3-GPI2) as compared with CAI4. The average of two experiments done in duplicate along with standard deviations are plotted. B, conditional null GPI2 mutant showed growth defect in the presence of 5 mm Met/Cys, which was more severe in the presence of 10 mm Met/Cys. The average of three experiments done in duplicate along with standard deviations are plotted. C, CAI4, GPI2 heterozygote, and the conditional null GPI2 mutant strains were analyzed for growth patterns on SD-minimal medium plates as described previously (6). The plates shown here are after 48 h of incubation at 30 °C. CAI4 and GPI2 heterozygote showed similar growth. However, the conditional null GPI2 mutant showed a growth defect dependent on Met/Cys concentration, thus correlating the effect to GPI2 expression from MET3 promoter. The experiment was done twice, and each time similar results were obtained; a representative image is shown. False color has been assigned to the image (using GIMP software), to brighten the cell spots. D, conditional null GPI2 mutant was assessed for viability using propidium iodide staining. Cells grown in absence of Met/Cys exhibited higher viability as compared with cells grown in the presence of 10 mm Met/Cys. Although 24% of cells grown in permissive medium (absence of Met/Cys) were stained with propidium iodide, 84% cells grown in repressive medium (10 mm Met/Cys) were found to be propidium iodide-stained (*, p value = 0.032). The experiment was repeated twice.