FIGURE 3.
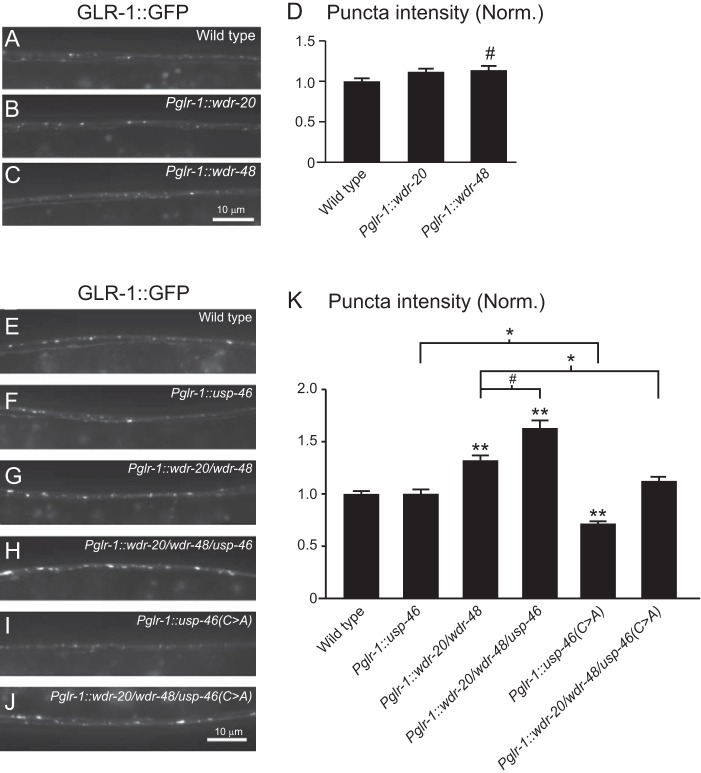
Effect of WDR-20, WDR-48, and USP-46 on GLR-1::GFP levels in vivo. A–C, representative images of the VNCs of L4 larval animals harboring a GLR-1::GFP transgene expressed under the control of the glr-1 promoter (nuIs24). The following genotypes are shown: wild-type (A), WDR-20 under control of the glr-1 promoter (pzEx230) (B), and WDR-48 under control of the glr-1 promoter (pzEx231) (C). D, quantification of GLR-1::GFP punctum intensities (normalized, norm.) for the strains pictured in A–C. Shown are the means ± S.E. for n = 38 (wild-type), n = 30 (Pglr-1::wdr-20), and n = 34 (Pglr-1::wdr-48). E–J, representative images of the VNCs of L4 larval animals harboring a GLR-1::GFP transgene expressed under the control of the glr-1 promoter (nuIs24). The following genotypes are shown: wild-type (E), usp-46 under the control of the glr-1 promoter (pzEx224) (F), wdr-20 and wdr-48 under the control of the glr-1 promoter (pzIs25) (G), wdr-20, wdr-48 and usp-46 under the control of the glr-1 promoter (pzIs25; pzEx224) (H), usp-46(C>A) under the control of the glr-1 promoter (pzEx222) (I), and wdr-20, wdr-48 and usp-46(C>A) under the control of the glr-1 promoter (pzIs25; pzEx222) (J). K, quantification of GLR-1::GFP punctum intensities (normalized) for the strains pictured in E–J. Shown are the means ± S.E. for n = 118 (wild-type), n = 56 (Pglr-1::usp-46), n = 76 (Pglr-1::wdr-20/wdr-48), n = 46 (Pglr-1::wdr-20/wdr-48/usp-46), n = 56 (Pglr-1::usp-46(C>A)), and n = 37 (Pglr-1::wdr-20/wdr-48/usp-46(C>A)). Values that differ significantly from the wild type (Tukey-Kramer) are indicated as follows: #, p < 0.05; *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001. Other comparisons are marked by brackets.