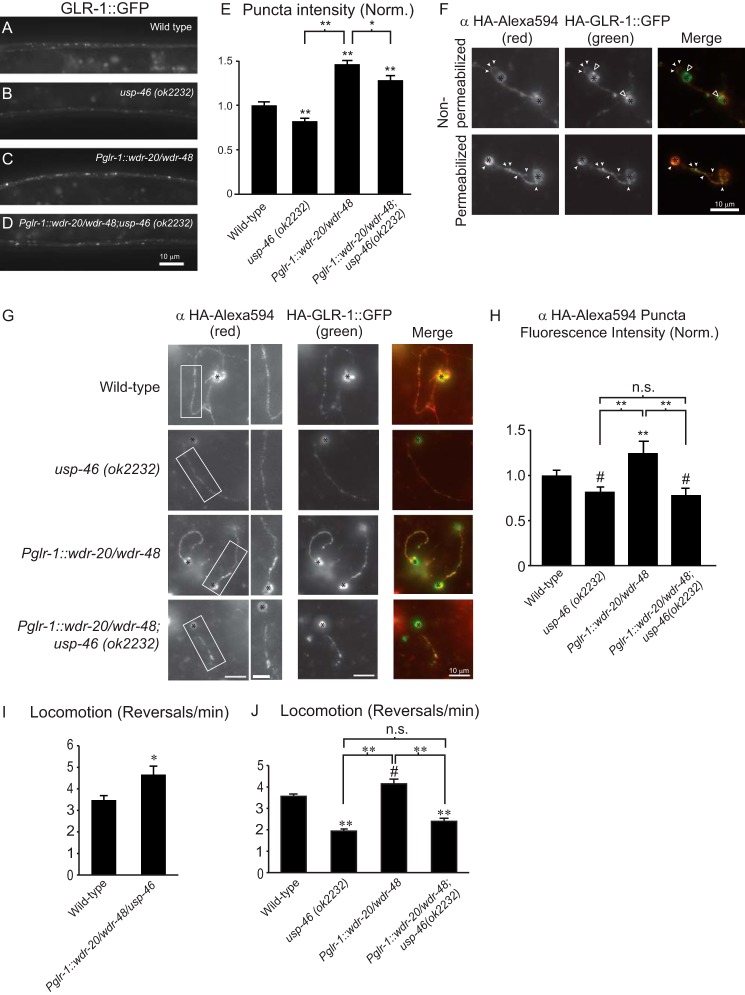
FIGURE 5.
Analysis of GLR-1::GFP abundance and glr-1-dependent behaviors in animals expressing WDR-20 and WDR-48 in the presence or absence of endogenous usp-46. A–D, representative images of the VNCs of L4 larval animals harboring a GLR-1::GFP transgene expressed under the control of the glr-1 promoter (nuIs24). The following genotypes are shown: wild-type (A), usp-46 (ok2232) (B), wdr-20 and wdr-48 under the control of the glr-1 promoter (pzIs25) (C), and wdr-20 and wdr-48 under the control of the glr-1 promoter (pzIs25) in the usp-46 (ok2232) mutant background (D). E, quantification of GLR-1::GFP punctum intensities (normalized, norm.) for the strains pictured in A–D. Shown are the means ±S.E. for n = 31 (wild-type), n = 36 (usp-46 (ok2232)), n = 34 (Pglr-1::wdr-20/wdr-48), and n = 35 (Pglr-1::wdr-20/wdr-48; usp-46 (ok2232)). F, representative images of primary, glr-1-expressing neurons isolated from wild-type C. elegans expressing HA-GLR-1::GFP (pzIs12). Cells were fixed under non-permeabilizing conditions (top row) or permeabilized (bottom row) and then fixed prior to immunostaining with anti-HA-Alexa Fluor 594 antibodies. Images of anti-HA-Alexa Fluor 594 staining (left column) and GFP (center column) are shown separately or merged (right column). White arrowheads indicate examples of anti-HA-Alexa Fluor 594-stained surface GLR-1 puncta that colocalized with the GFP signal of HA·GLR-1::GFP. Open arrowheads indicate internal GLR-1::GFP in the non-permeabilized cell bodies. The black asterisks mark cell bodies. G, representative images of primary neurons from animals of the indicated genotypes. Cells were fixed and stained with anti-HA-Alexa Fluor 594 antibodies under non-permeabilizing conditions. Images of anti-HA-Alexa Fluor 594 immunostaining with higher magnification images of the boxed regions (left column) or GFP (center column) are shown separately or merged (right column). Black asterisks mark cell bodies. H, quantification of anti-HA-Alexa Fluor 594 punctum intensities relative to the interpunctal intensity of the neurite (normalized). Means ± S.E. are shown for individual neurites analyzed. n = 48 (wild type), n = 22 (usp-46 (ok2232)), n = 35 (Pglr-1::wdr-20/wdr-48), and n = 35 (Pglr-1::wdr-20/wdr-48; usp-46 (ok2232)). I, average number of reversals per minute for spontaneous locomotion assays performed on animals of the following genotypes: n = 14 (wild type) and n = 15 (Pglr-1::usp-46/wdr-20/wdr-48). J, average number of reversals per minute for spontaneous locomotion assays performed on worms of the following genotypes: n = 37 (wild type), n = 37 (usp-46 (ok2232)), n = 38 (Pglr-1::wdr-20/wdr-48), and n = 37 (Pglr-1::wdr-20/wdr-48;usp-46 (ok2232)). Values that differ significantly from the wild type (Tukey-Kramer test) are denoted above each bar. Other comparisons are marked by brackets. #, p < 0.05; *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001; n.s., no significant difference between the indicated strains (p ≥ 0.05). Error bars show S.E.