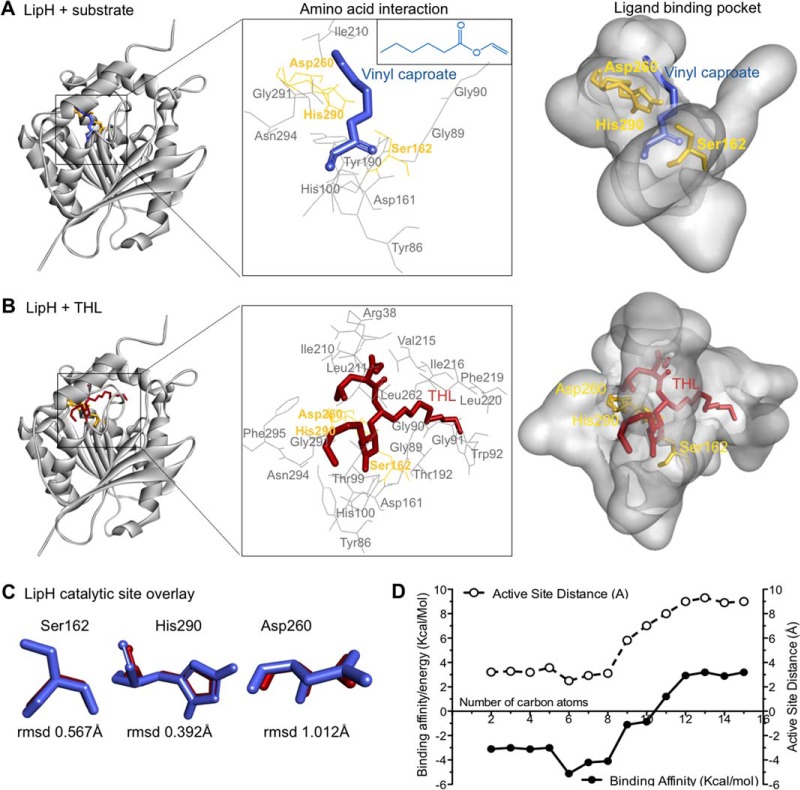
Fig. 4.
Molecular examination of natural substrate recognition and mimicry by THL. A and B, Three-dimensional model of the LipH structure depicting the core α/β-hydrolase fold with catalytic triad (yellow). Vinyl caproate (blue, insert E), a described substrate of LipH in vitro, and THL (red) are docked to the active site using computational methods. The insert (middle) depicts the catalytic triad and other amino acids interacting with docked ligands. C, Overlay of catalytic triad shows the individual amino acid conformation when LipH is docked with vinyl caproate (blue) and with THL (red), respectively. The root mean square deviations (rmsd) of the differences between vinyl caproate and THL predictions are indicated at the bottom. D, Plot depicting the change in binding energy (Kcal/mol) and distance to active site serine (Å) when vinyl esters of different chain lengths are docked with the LipH 3D-model.