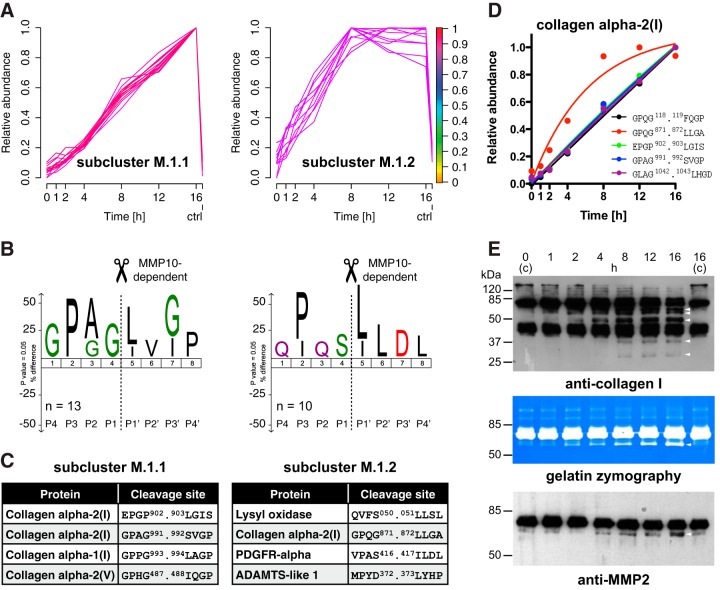
Fig. 5.
Subclassification of MMP10-dependent cleavage events. A, Subclustering of MMP10-generated neo-N termini. Peptides assigned to cluster M.1 with a membership value of ≥0.9 were assigned to two subclusters with slow and fast increase in abundance on MMP10 incubation. Colorkey indicates membership value α. ctrl: 16 h control. B, IceLogo analysis of cleavage sites corresponding to peptides assigned to subcluster M.1.1 and subcluster M.1.2, respectively. Low efficient cleavages in subcluster M.1.1 resemble the typical MMP cleavage motif GPXG.L/I in collagens. P in P3 and/or L/I in P1′ for cleavages in subcluster M.1.2 indicate MMP-dependent cleavage events. C, Examples for proteins and MMP10-dependent cleavages in each subcluster. Predominant assignments of collagens to subcluster M.1.1 demonstrate slow processing of these structurally occluded cleavage sites. Only the canonical MMP cleavage site in the type I collagen α2 chain is processed with high efficiency as indicated by assignment to subcluster M.1.2. See supplemental Table S9 for a full list of MMP10-dependent cleavages. D, Kinetic profiles of cleavages in the collagen α2(I) chain. Time-resolved subclustering distinguished the canonical MMP cleavage site (red) from additional MMP10-dependent cleavages within the same collagen chain. E, Validation of multiple processing of type I collagen and concomitant increase in abundance of active MMP2. Upper panel: Immunoblot analysis of MMP10 incubated secretomes from Mmp10−/− MEFs using an anti-collagen I antibody showed appearance of cleavage fragments (arrows) with distinct kinetic profiles. Middle panel: Gelatin zymography revealed MMP10-dependent increase in abundance of a band matching the size of activated MMP2 (arrow) in MMP10-incubated secretomes. Lower panel: Immunoblot analysis of the same samples using an antibody directed against MMP2 confirmed time-dependent activation of MMP2 (arrow) on MMP10 incubation.