Figure 1. Scanning White Light Interferometer set-up that compensates for the microfluidic channel roof (Left).
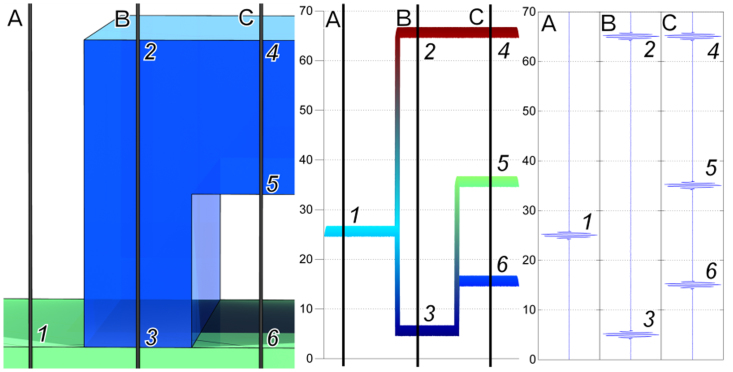
The geometric thickness (dg) of the polymer layer is A1-B2 since the refractive index of air = 1. The effective refractive index of the adhered layer is (B3-B2)/(A1-B2). The same approach can be used to determine the height of disbonds. The method provides 10–20 nm traceable resolution along the z-dimension. It can measure stacked layers that are static or moving10. It can determine a Sq parameter (ISO 25178) that potentially can be linked to Rq even inside a microfluidic channel without direct tactile access.