Figure 3. RNAi factors associate in multi-protein complexes in the nucleus.
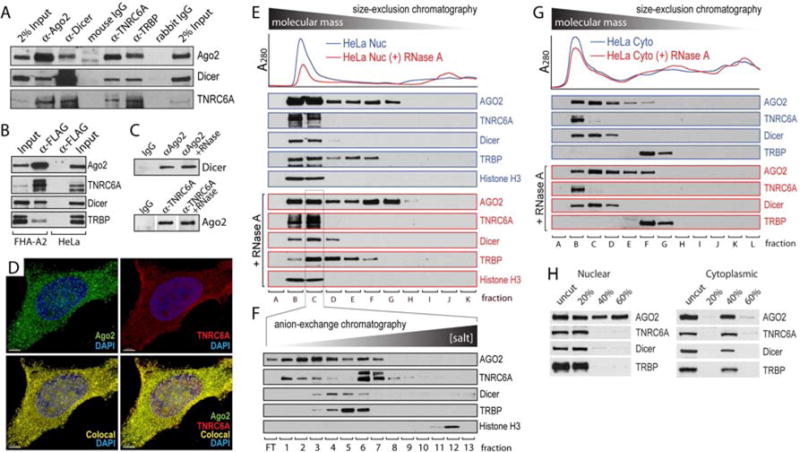
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) of endogenous RNAi factor from HeLa nuclear extract. The antibodies used for the western blot detection are noted the right while the antibodies used for immunoprecipitations are on top. (B) Co-IP of RNAi factors from T47D cells expressing FLAG-HA-tagged Ago2 (FHA-A2). HeLa nuclear extract serves as a negative control. Input is extract prior to immunoprecipitation. (C) Co-IP of Ago2 with Dicer or TNRC6A from T47D nuclear extracts treated with RNase A. (D) Immuno-fluorescence of Ago2 and TNRC6A in HeLa cells indicates overlap and co-localization of immuno-staining. Z-stacks (3 μm of 0.1 μm slices) are projected in 3D. The co-localization channel was generated in Imaris (Bitplane). Scale bar = 5 μm. (E) Western analysis of fractions from separation of HeLa cell nuclear extract by size exclusion. Extracts were prepared either with our without treatment by RNAse A. Western blot antibodies are shown to the right. Sample fractions are below. Histone H3 is marker for high molecular weight chromatin. (F) Western analysis of fractions after anion-exchange chromatography of nuclear extract Fraction C from Figure 5E. FT, column flow-through. (G) Western analysis of fractions HeLa cytoplasmic extract after size exclusion chromatography. Extracts were prepared either with our without treatment with RNase A. (H) Effect of ammonium sulfate precipitation of RNAi factors from T47D nuclear or cytoplasmic extracts. Western blot antibodies are shown to the right and ammonium sulfate concentrations (% saturation) are shown above.
