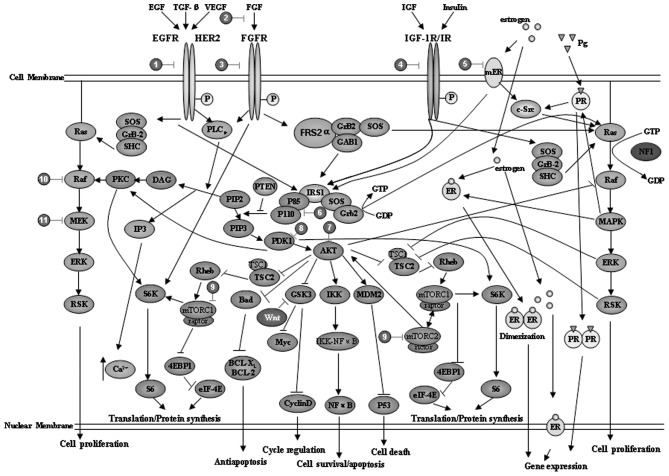
Figure 2.
Crosstalk of signaling pathways in breast cancer and the potential clinical therapeutic targets. The receptors of extracellular small molecules shown here include: epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, insulin and estrogen, which activate their corresponding receptors and further transduce the signals mainly through the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway or the Ras/MEK pathway. A number of PI3K/AKT and Ras/MEK signaling pathway inhibitors have been developed, some of which may be used in combination (details also summarized in Table II). Pg, progesterone; ER, estrogen receptor; PR, progesterone receptor; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; RSK, ribosomal S6 kinase; IP, inositol phosphate; PKC, protein kinase C; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; PDK, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase.