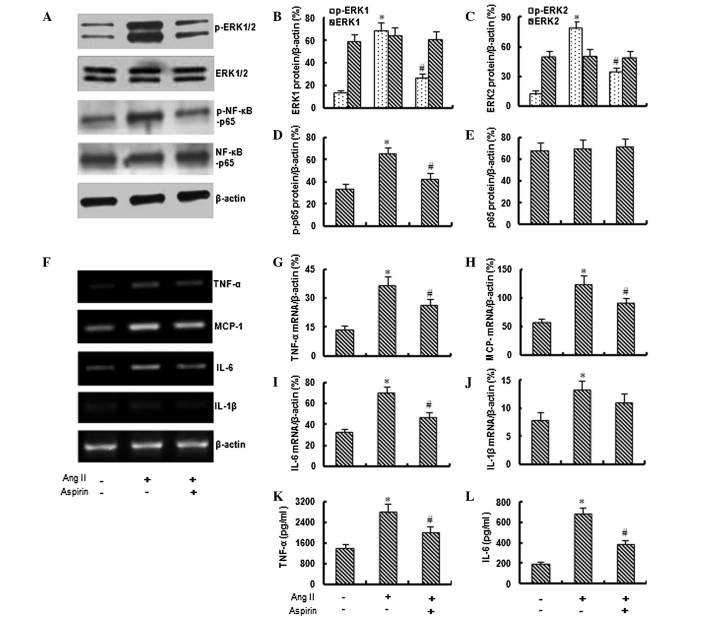
Figure 2.
Aspirin inhibits angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced inflammation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (bmMSCs). (A–E) Western blotting demonstrated that aspirin (0.1 mM) inhibits the Ang II (1 μM)-induced expression of phospho-extracellular signal-regulated protein-1/-2 (p-ERK1/2) and phospho-nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (p-NF-κB) in bmMSCs. (F–J) The reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay demonstrated that aspirin inhibits the Ang II-induced expression of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) in bmMSCs. (K,L) The ELISA demonstrated that aspirin inhibits the Ang II-induced secretion of TNF-α and IL-6 from bmMSCs. The bar graphs represent means ± SD (4 independent experiments/group). *P<0.05 vs. control and #P<0.05 vs. Ang II.