Abstract
Background: Pain plays roles in both the nervous system and immune system. Changes in the neuroendocrine pathway under pain conditions give rise to sympathetic outflow with increased plasma catecholamines and activate immune reactions. Dexmedetomidine exerts sedative, analgesic, and anesthetic-sparing effects and is known to diminish pro-inflammatory processes by central sympatholytic effects. To investigate the influence of the analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine on immunomodulation under pain conditions, splenic natural killer (NK) tumoricidal cytotoxic activity, proliferative ability of T lymphocytes, and cytokine changes were assessed.
Methods: After evaluation of the analgesic efficacy of dexmedetomidine in C57BL mice that were subjected to formalin-induced pain, dexmedetomidine (30 µg/kg) or saline was injected intraperitoneally (ip) 30 min before formalin (20 µL of 2% formalin in 0.9% saline) injection. NK cell activity against NK-sensitive YAC-1 lymphoma cells was evaluated by the percentage of specific lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. Various numbers of effector cells (NK cells) were added to the wells of a microtiter plate containing 2 × 104 target YAC-1 cells in 100 μL, to achieve final effector-to-target cell ratios of 80:1, 40:1, and 20:1. The level of lymphocyte proliferation in response to phytohemagglutinin (PHA) was detected by bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation assay. TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-10 levels were determined in blood samples and supernatants of splenocyte preparations.
Results: IP administration of dexmedetomidine significantly decreased the time of licking and biting during the first and second phases of the formalin test (p <0.001). Formalin-induced pain led to higher activity of NK cells than in sham-treated mice (p <0.05), but NK activity was not increased significantly by ip dexmedetomidine treatment. Formalin-induced pain significantly increased splenic lymphocyte proliferation (p <0.05), but dexmedetomidine did not alter this response. There was a significant increase in plasma TNF-α (p = 0.048) and IL-6 (p = 0.014) levels after formalin-induced pain. However, the differences between the responses after ip dexmedetomidine did not change significantly.
Conclusions: Dexmedetomidine showed antinociceptive effect on both of acute pain phase 1 and hyperalgesic phase 2 of formalin pain model. Formalin-induced pain alters cellular immunity of spleen in mice. Dexmedetomidine attenuates the activation of NK cells under pain condition, but neither the proliferative response of the splenic lymphocytes nor the cytokine production was affected by dexmedetomidine.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine, Antinociceptive Effect, Cell Immunity, Mice
INTRODUCTION
A complex interaction occurs between the sympathetic nervous system and the immune system. The immune system detects pain or concomitant tissue injury through nociceptor-induced sympathetic activation, because immune cells of lymphoid organs express adrenorecptors 1. Generally, pain enhances the cytotoxic activity of natural killer (NK) cells, the lymphoproliferative response of lymphoid tissue, and cytokine production by immune cells 2,3. In the immune-nervous system interaction, reducing the sympathetic outflow after pain or tissue injury can modulate immune activity 1,4
Dexmedetomidine, a potent α-2 adrenergic agonist, reduces central sympathetic outflow. It has been used clinically for anxiolysis, analgesia, sedation, and anesthetic sparing 5,6. Hemodynamic profiling in animal models has demonstrated that dexmedetomidine improves endotoxin-induced shock and increases survival rates by diminishing the pro-inflammatory process via central sympatholytic effects 7,9. However, whether the analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine modulates cell-mediated immunity has not been determined.
We investigated the influence of the analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine on immunomodulation under pain conditions. Specifically, we assessed splenic NK tumoricidal cytotoxic activity and the proliferative ability of T lymphocytes among splenocytes from mice undergoing formalin-induced pain.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
All experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, CIMC-2012-010). All procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines specified in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH publication no. 86 to 23, revised 1985) as well as the Ethical Guidelines for Investigations of Experimental Pain in Conscious Animals.
Animals
Specific pathogen-free male C57BL/6NCrlCrljori mice (20-25 gm, 4-6 weeks old) were purchased from OrientBio, Inc. (Seoul, Korea). The animals were acclimatized for 1 week before the experiments in an air-conditioned barrier-system room and were allowed free access to standard rodent chow and tap water. Mice were housed together under standard conditions, i.e., a reverse daylight pattern maintained through artificial illumination and a constant temperature and relative humidity (20-25°C and 50%±10%) respectively. The mice were divided into four groups (n=7): saline or dexmedetomidine hydrochloride treated formalin injection group (F-Sal and F-Dex) and saline or dexmedetomidine hydrochloride treated saline injection group for sham control group (Sham-Sal and Sham-Dex).
Formalin test and drug administration
Mice were individually placed in transparent observation chambers (200×100×130 mm) for adaptation 40 min before testing. Then, the animal was taken out of the chamber, and volume of 10 mL/kg of dexmedetomidine (30 µg/kg) (Orion Pharma, Espoo, Finland) intraperitoneally (ip) or physiological saline was injected (ip). After 30 min of dexmedetomidine ip injection, 20 µl of 2% formalin in 0.9% saline in a micro-syringe was injected subcutaneously (sc) into the dorsal surface of the right hindpaw with a 30-gauge needle 10 under isoflurane anesthesia. Saline was injected in sham control group. Immediatedly after formalin or saline injection, each mouse was returned to the observation chamber. The amount of time spent licking and biting the injected paw was considered as indicative of pain and was measured with a hand-held stopwatch during the first phase (from 0 to 10 min) and the second phase (from 10 to 30 min).
In vitro cytotoxicity and cell vitality assay
First, we evaluated spleen cell vitality in vitro whether the chemical can be toxic to cells directly. The number of viable cells with dexmedetomidine during cell proliferation was determined. We utilized highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt by the application of the colorimetric cell counting kit (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). WST-8[2-(2-methoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(2,4-isulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, monosodium salt] is reduced by dehydrogenases in cells to give an orange colored product (formazan), which is soluble in the tissue culture medium. Hence, the increase of the amount of the formazan dye generated by dehydrogenases is directly correlated with the number of metabolically active living cells 11. Splenic cell suspension (1×104 cells/100 µl) in a 96-well plate was pre-incubated in a humidified incubator (5% CO2 & 37°C) for 48 h. Followed by adding various concentrations of dexmedetomidine (10, 5, 1, 0.1 and 0.01 µM, 10 µl), cells were incubated again for 48 h. Only PBS was mixed with cell culture medium in negative control wells. WST-8 solution (10 µl) was added to each well and the plate was incubated for 4h. The absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader.
Cell preparation
Mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation after assessing the pain behavior of formalin test. The spleen was aseptically excised and stored in tissue culture medium (RPMI 1640; Gibco BRL, Grand Island, NY). A single-cell suspension was made by using a 5-mL syringe plunger to pass spleen tissue in fresh wash medium through a 70-μm mesh strainer (BD Falcon, San Diego, CA). Splenocytes were suspended in complete RPMI medium (RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 units/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin, and 2 mM L-glutamine). Cell number and viability were estimated using a hemocytometer, and trypan blue exclusion to identify dead cells.
NK cell cytotoxic activity assay
The tumoricidal activity of NK cells from the spleen of each mouse was determined by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity using cytotoxicity detection kit. YAC-1 cells (mouse lymphoma cells) were used for target cells of NK cells. LDH is a stable cytopalsmic enzyme present in all cells and LDH assay is an alternative to the previous radioactive 〔3H〕-thymidine release or the 〔51Cr〕-release assay. This is colorimetric assay for the quantification of cell death or cell lysis, based on the measurement of LDH activity released from the cytosol of damaged cells into the supernatant using spectrophotometric microplate reader 12.
YAC-1 lymphoma cells were grown in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with antibiotics and 10% fetal bovine serum. Effector splenocyte suspensions were prepared from each mouse, and various numbers of effector cells were added to the wells of a microtiter plate containing 1 × 104 target YAC-1 cells in 100 μL, to achieve final effector-to-target cell ratios of 80:1, 40:1, and 20:1. The plates were incubated for 4 h at 37°C in 5% CO2 at 90% humidity. Then, the cells were removed by centrifugation, and the supernatants were collected and transferred to a flat-bottom plate. After 100 μL of freshly prepared LDH detection mixture were added to each well, the plate was incubated at room temperature for 30 min to permit color development. The absorbance in each well was measured at 490 nm with a plate reader, and the percentage of specific LDH release was determined according to the following equation:
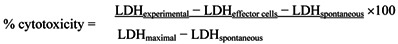 |
LDHexperimental: release from co-culture of effector cells and target cells
LDHeffector cells: release from separately cultured effector cells
LDHspontaneous: release from separate cultures of YAC-1 cells (low control)
LDHmaximal: release from total lysis of YAC-1 cells by Triton X-100 (high control)
Mitogenic stimulation assay for splenocytes proliferation
The immunoreactivity of isolated splenocytes from each mouse was determined by the level of proliferative responses to mitogenic stimulation using phytohemagglutinin (PHA). It was measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit for bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) detection (Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Mannheim, Germany). This is colorimetric alternative to quantify cell proliferation based on the measurement of BrdU incorporation in newly synthesized cellular DNA 13. Splenocytes from each mouse were counted, and the concentration was adjusted to 1 × 105 cells/100 μL. Aliquots (200 μL, 2 × 105) of cells were added to the wells of a 96-well flat-bottom plate and cultured at 37°C in 5% CO2 at 90% humidity in the presence of PHA for 48 h with 5 μg/100 μL of PHA added every 24 h. For pulse-labeling, 10 μL of BrdU were added to each well (10 μM final concentration), and were incubated for 18 h. The labeling medium was removed using a needle, and the cells were air-dried. Then, 200 μl of FixDenant agent were added per well to fix the cells and denature the genomic DNA, thereby exposing the incorporated BrdU to immunodetection. After incubation for 1 h at room temperature, the fixative was removed, 100 μL of horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-BrdU antibody (clone BMG 6H8, Fab fragment) were added to each well, and the plate was incubated at room temperature for 90 min. The wells were then washed three times with phosphate-buffered saline, and 100 μL of tetramethylbenzidine substrate were added. The plate was incubated at 25°C for 20 min, and the absorbance was measured at 370 nm with an automated plate reader. Proliferation was determined as the stimulation index (SI), calculated as follows:
| SI = ODStimulated well /ODUnstimutaled well |
OD: optical density
In vitro splenocytes proliferation
For evaluation of direct influence of dexmedetomidine on splenic proliferation, in vitro levels of BrdU were measured. Different concentrations of dexmedetomidine (0.1, 1, 5 and 10 µM) were added to the wells containing splenocytes and cells were cultured for 24 h. After washing, cells were counted and adjusted as 2 × 105 cells/200 μL. Aliquots of cells were added to the wells of a 96-well flat-bottom plate and cultured at 37°C in 5% CO2 at 90% humidity for 48 h. PHA (5 µg/100uL) was added every 24 hr and 10 μL of BrdU were added to each well (10 μM final concentration). After 18 h incubation, cell proliferation was also measured under the absorbance of 370nm with an automated plate reader.
Quantitative detection of cytokines in vivo and in vitro
Blood samples and supernatants of splenocytes preparation
Blood samples were obtained by exsanguinating mice under isoflurane anesthesia after formalin test. Samples were centrifuged (3000g, 15 min, 4 ℃). Plasma was stored at - 80 ℃ until measurement of cytokines.
The supernatants from each isolated splenocytes were collected after cell proliferation with PHA. The concentration of splenocytes was adjusted to 1 × 105 cells/100 μL. Aliquots (200 μL) of cells were added to the wells of a 96-well flat-bottom plate and cultured at 37°C in 5% CO2 at 90% humidity in the presence of PHA. Five μg of PHA was added every 24 h to the wells. After 2 days incubation, the supernatant from each well were collected and stored at - 80 ℃ until being used for cytokine assay.
Cytokine production assay
The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-10 were determined using ELISA kits (R&D systems, Minneapolis). Aliquots (50 μl) of each standard, control and samples were added to the designated wells, followed by 50 μl of assay diluents. The plates were incubated for 2 hours with covering adhesive film at room temperature on a horizontal orbital microplate shaker. After washing of unbound materials, 100 µL of conjugate was added to each well and incubated for 2 h on the shaker. Substrate solution (100 µL) was added after aspiration and washing 4 times, and the plates were incubated at room temperature for 30 min with protecting from light. Stop solution (100 µL) was added to each well and the plate was red at 450 nm within 30 min.
Statistical analysis
Data are reported as means ± SD. All results were analyzed using Sigma-Stat version 2.03 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL). Mann-Whitney rank sum test was used to analyze the behavioral experiment. Two way analysis of variance followed by the Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons was applied to compare NK cell cytotoxicity. The Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA by ranks was performed followed by the Tukey method for multiple comparisons to evaluate the difference in the splenocyte proliferative response, in vitro study and cytokine response among groups. Statistical significance was accepted at P < 0.05.
RESULTS
Dexmedetomidine exhibits an analgesic effect in mice with 2% formalin-induced pain
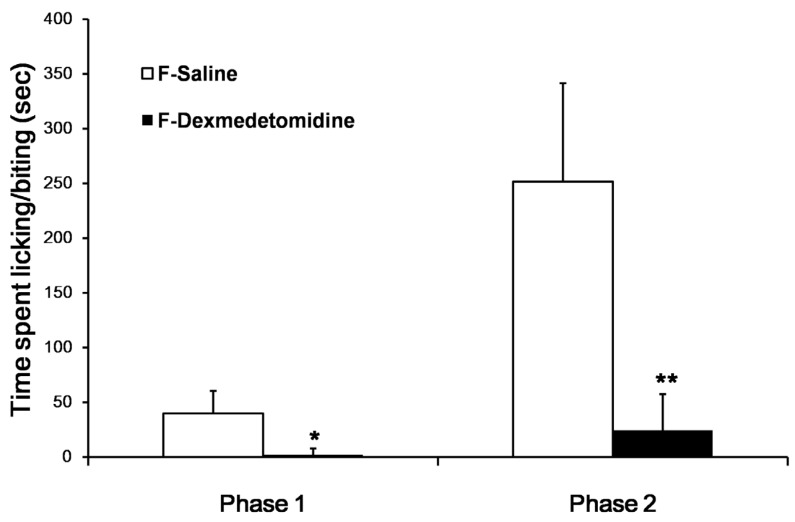
Subcutaneous injection of 2% formalin into the dorsal surface of the hind paw produced biphasic pain behaviors, which consisted of licking and biting of the injected paw. Formalin injection with ip saline group (F-Sal) induced 39.7 ± 20.7 and 251.7 ± 89.8 s of licking and biting during the first and second phases, respectively. In contrast, formalin injection with ip dexmedetomidine group (F-Dex) significantly decreased the licking and biting time in both the first and second phases (1.1 ± 2.2 and 24.5 ± 33.0 s, respectively; Fig. 1). (P < 0.001)
Fig 1.
Effect of dexmedetomidine in mice experiencing 2% formalin-induced pain. The total time spent licking and biting the injected paw was measured during the first phase (0-10 min) and second phase (10-30 min) after subcutaneous injection of formalin into the dorsal surface of the hind paw. Dexmedetomidine (30 µg/kg) administered intraperitoneally (ip) 30 min before formalin injection produced significant antiallodynic effects. The data are presented as means ± SD of seven mice. *p <0.001 versus saline group. **p <0.001 versus the saline group. F: formalin
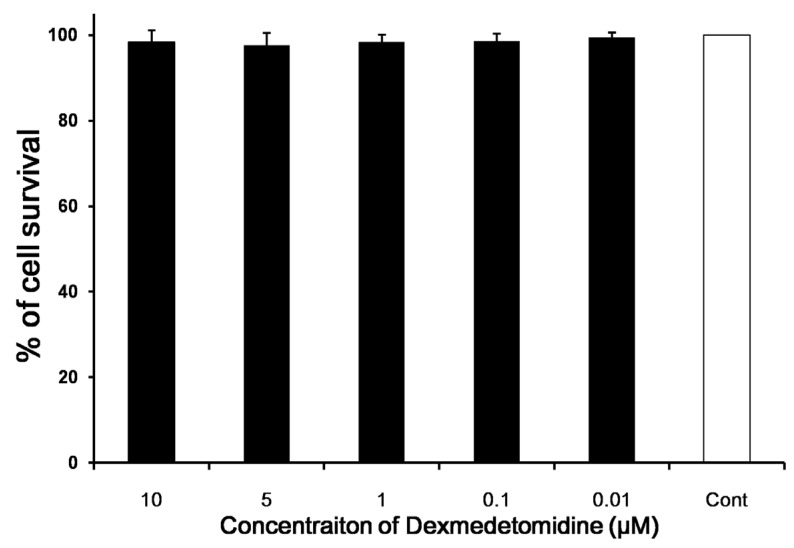
Dexmedetomidine is non-cytotoxic in cell viability assay
We investigated whether dexmedetomidine exerted a direct cytotoxic effect on splenocytes. The cell survival rates were determined in comparison with a negative control. Cell survival rate was affected negligibly according to dexmedetomidine concentration (P = 0.159) (Fig. 2).
Fig 2.
In vitro cytotoxicity and cell viability assays. The direct cytotoxic effect of dexmedetomidine on splenocytes was assayed using highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt and a colorimetric cell-counting kit. The cell survival rate relative to the negative control changed only negligibly with increasing dexmedetomidine concentration. Data represent means ± SD.
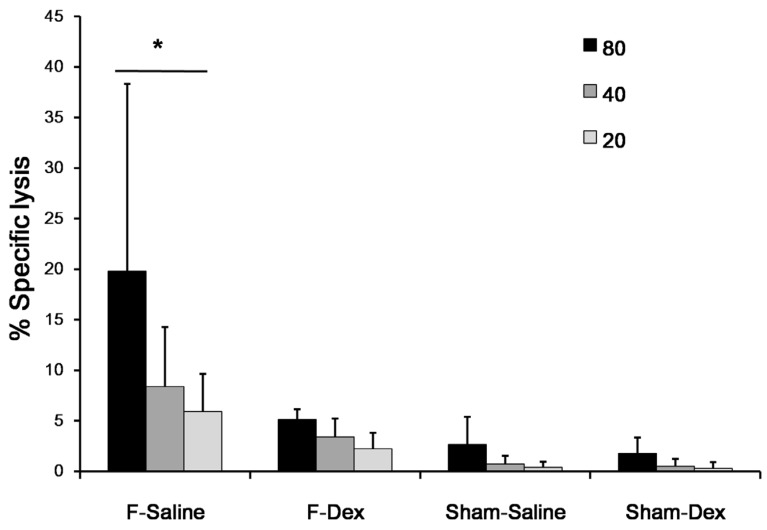
Dexmedetomidine prevents NK cell activation in formalin-treated mice
The tumoricidal activity of NK cells against NK-sensitive YAC-1 lymphoma cells from each mouse was assessed. The results are shown as plots of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release (Fig. 3). Formalin induced pain (F-Sal) led to higher NK cytotoxic activity among groups (P < 0.05). Intraperitoneal injection of dexmedetomidine (F-Dex) significantly decreased NK cytotoxic activity compared to ip saline injection in formalin groups (F-Sal)(P < 0.05). Specifically, at an 80:1 ratio of NK cells to NK-sensitive YAC-1 lymphoma cells, NK cell activities were 19.8 ± 18.5% in cells from F-Sal group, 5.1 ± 0.9% in cells from F-Dex group, 2.6 ±2.7% in cells from Sham-Sal group, and 1.7 ±1.5% in cells from Sham-Dex group.
Fig 3.
Effect of dexmedetomidine on splenic NK cell cytotoxic activity. Spleen cells were isolated from sham (Sham-Dex, dexmedetomidine-treated; Sham-Saline, saline-treated) control mice, and mice subjected to formalin-induced pain (F-Dex, dexmedetomidine-treated; F-Saline, saline-treated). The tumoricidal activity of NK cells against NK-sensitive YAC-1 lymphoma cells was evaluated. Cells were cultured in the presence of YAC-1 target cells (at varying effector-to-target [E:T] ratios), and co-cultures were assessed for lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. The percentage of LDH released reflected NK cytotoxic activity. Data represent means ± SD of seven mice. *p <0.05, with correction for multiple comparisons. F: formalin, Dex: dexmedetomidine
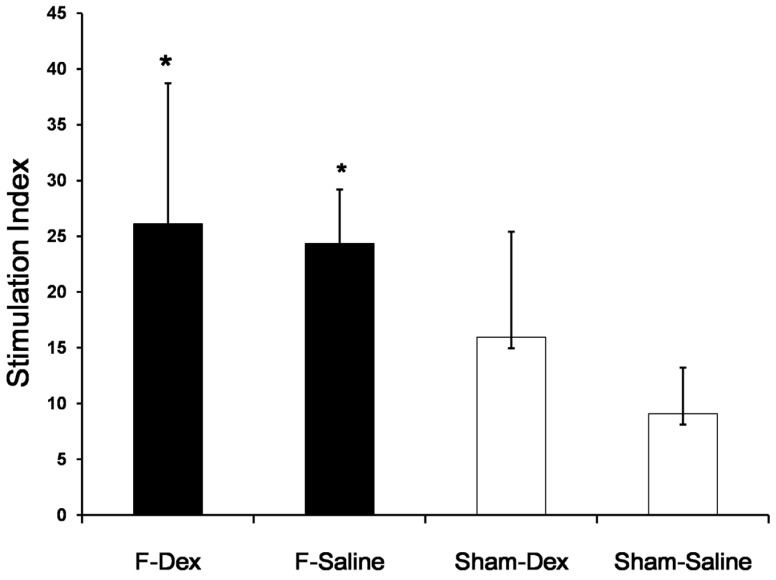
Dexmedetomidine did not alter the proliferative response of splenic lymphocytes in formalin-induced pain
The proliferative response of splenic lymphocytes to PHA, as determined by ELISA, is shown as a stimulation index plot (Fig. 4). Formalin-induced pain in both of ip saline (F-Sal) and ip dexmedetomidine (F-Dex) group significantly increased splenic lymphocyte proliferation compared to Sham groups (P < 0.05). However, no significant difference was found between ip dexmedetomidine and ip saline treatment in formalin groups.
Fig 4.
Effect of dexmedetomidine on proliferative response of splenic lymphocytes. Spleen cells were isolated from sham (Sham-Dex, dexmedetomidine-treated; Sham-Saline, saline-treated) control mice, and mice subjected to formalin-induced pain (F-Dex, dexmedetomidine-treated; F-Saline, saline-treated). Immunoreactivity was determined by the proliferative response to phytohemagglutinin (PHA) as a mitogen. Proliferation was measured by BrdU detection and reported as the stimulation index (SI). Data represent means ± SD of seven mice. *p <0.05 versus Sham-Saline, with correction for multiple comparisons. F: formalin, Dex: dexmedetomidine
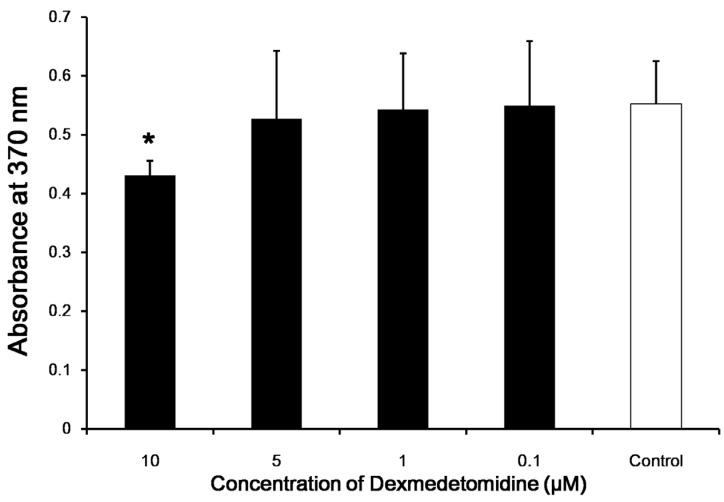
For in vitro evaluation of splenocyte proliferation, the levels of BrdU after application of 0.1, 1, and 5 µM dexmedetomidine were not different from that of the control; however, there was a significant difference with 10 µM dexmedetomidine (P < 0.05; Fig. 5).
Fig 5.
In vitro splenocyte proliferation. BrdU incorporation by splenocytes from negative control and splenocytes treated with various dexmedetomidine concentrations were determined in vitro. Data represent means ± SD and are reported as optical density (OD) values. *p <0.05 versus control with correction for multiple comparisons.
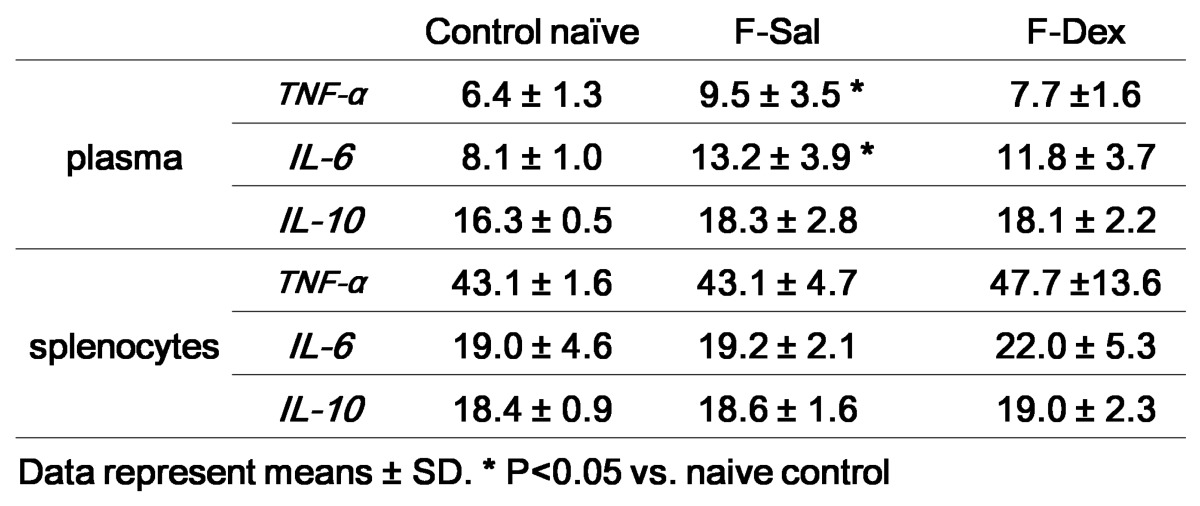
Effect of Dexmedetomidine on the Level of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-10 of plasma and splenic lymphocytes
The results obtained from the evaluation of cytokine secretion from plasma and proliferated splenic lymphocytes were summarized in Table 1. There was significant increase in plasma TNF-α (P=0.048) and IL-6 (P=0.014) after formalin induced pain. But, the differences between the responses after ip dexmedetomidine (F-Dex) in each case were not significantly changed compared to control naive. TNF-α or IL-6 from the supernatant in splenic lymphocytes proliferation was not different among group. IL-10 from plasma or supernatant of was not different among groups.
Table 1.
Cytokine repertoire of plasma and isolated splenocytes (pg/ml)
DISCUSSION
We evaluated the influence of the analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine on formalin-induced pain and its impact on spleen cell immunity in mice. The formalin pain model provides a validated model of inflammatory pain. In clinical situations, inflammation contributes to both postoperative pain and hyperalgesia. We showed the biphasic pain response of the formalin test and demonstrated the antinociceptive effect of dexmedetomidine on both acute pain (phase 1) and hyperalgesia (phase 2).
Dexmedetomidine induces dose-dependent, age-independent antinociception in experimental animals. Its analgesic effect is mediated via α-2A adrenoceptors, which are thought to reduce excitatory neurotransmission. In addition to acting on the spinal cord 14, which is associated with primary afferent nociceptive neurons, it also acts supraspinally in the locus ceruleus, which has functional connectivity between descending inhibitory neurons and higher centers 15.
Pain plays roles in both the nervous system and immune system. Changes in the neuroendocrine pathway under pain conditions give rise to sympathetic outflow with increased plasma catecholamines. Results regarding immune responses to pain have been controversial. However, the complex interaction between the sympathetic nervous system and cellular immunity affects immune reactivity, leading to the activation of lymphoid organs and the expression of various hormone receptors on immune cells. Generally, pain and stress augment NK cell activity and lymphoproliferation 1,4.
NK cell cytotoxic activity is commonly used to evaluate cellular innate immunity in tumor surveillance and antibacterial activity 16. The increased NK cell activity and lymphocyte proliferation provoked by pain induced by formalin injection described here are similar to previous reports of acute pain responses 14; however, in the present study, NK cell cytotoxicity was inhibited by dexmedetomidine treatment.
The reason for reduced NK cell cytotoxicity upon dexmedetomidine treatment is not known, but with regard to its influence on the immune system, Inada 17 reported that treatment with a subhypnotic dose of dexmedetomidine down-regulated acquired antitumor immunity and decreased cytokine production. In addition to the direct effect of dexmedetomidine on immune cells, an indirect effect on immune cells through inhibition of norepinephrine output from nerve terminals might also be involved in the reduction of the response 5. However, discordance between the analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine and the inhibited NK cell activity adds complexity to the mechanisms of pain perception and immunity in different subjects 2 and may not be part of an analgesic response 18.
T-lymphocyte proliferation is a common test of T-cell responsiveness. The mechanism(s) underlying stress-induced changes in the lymphocyte response to mitogens remains unknown, but the phenomenon has been documented in animals. Blood epinephrine and adrenal cortical hormone levels, which change according to the degree of stress or pain, might determine the activation of T lymphocytes 19. The proliferative response to formalin-induced pain shown by our results is consistent with such stress-induced changes 2,3.
Interestingly, the analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine did not affect lymphocyte proliferation, which is similar to a report that dexmedetomidine did not attenuate lymphocyte proliferation in a dose-dependent manner in a bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation assay 20. In vitro, the proliferative response was not directly affected by dexmedetomidine, except at high concentrations (10 µM). It is also known that dexmedetomidine exerts neuroprotective effects in vitro at the higher concentration of 100 µM 21. The clinically acceptable concentration is the lower end of the range used in our study, which did not affect proliferation in vitro. Dexmedetomidine is preferable for immunocompromised patients, because neither lymphocyte dysfunction nor attenuated lymphocyte proliferation was found at clinically relevant plasma concentrations 20. While dexmedetomidine showed age-dependent hypnotic sensitivity, as demonstrated by potent hypnosis in neonatal rats 22, it is subhypnotic to mice at a dose of 50 µg/kg 23. The dose used in this study was lower than 50 µg/kg and exerted an antinociceptive effect on formalin-induced pain.
Several explanations for the discrepancies between our results and those of other investigators are possible. The acute increase in proliferation by acute stress or pain returns to control levels after a relatively short period 2; we evaluated the proliferative response 1 h after treatment, which may have been too soon to detect effects on splenic lymphocytes. Moreover, we assessed only splenic lymphocyte proliferation; thus, any altered trafficking or redistribution of lymphocytes within lymphoid organs outside of the spleen would not have been detected 24.
Preservation of the innate immune response with dexmedetomidine sedation was evidenced by a drastic reduction in mortality rates due to sepsis and trauma in both animal models and human patients 9,25. Plasma TNF-α and IL-6 levels are predictive of mortality in septic conditions 26. The increased plasma TNF-α and IL-6 levels after the formalin test we report here correspond well with the results of a previous study, which reported that plasma cytokine activities were affected by pain 2. Dexmedetomidine has been reported to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine production 27,28; however, the mechanism underlying the improvement of mortality due to sepsis is not established. It may be related to its central sympatholytic effects 8,25. Dexmedetomidine can influence both inflammation (in the early phase of sepsis) and apoptosis (in the later phase of sepsis) 7. Dexmedetomidine treatment also inhibited the augmentation of plasma TNF-α and IL-6 levels in the current study.
Sharify 2 suggested that use of different shock paradigms and experimental protocols affects the measurement of immune system function. In animal models, immune function is altered by exposure to stimuli such as loud noises 29, foot-shock and shaking 30, and surgery 31. Whether the altered immune reaction after dexmedetomidine administration is advantageous from the point of view of ongoing pain is not clear. However, analgesics have various effects on immune reactivity, and the impact of acute or chronic use of analgesics could be important. Selection of appropriate analgesics and the time of prescription initiation might influence the normal immune response to invading microorganisms or tumor surveillance. Further investigation is required to elucidate the site(s) and mechanism(s) of the immunomodulatory effects of dexmedetomidine.
CONCLUSION
Dexmedetomidine showed antinociceptive effect on both of acute pain phase 1 and hyperalgesic phase 2 of formalin pain model. Analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine modulates cellular immunity of spleen in mice. NK cell activation by formalin-induced pain was inhibited by dexmedetomidine; however, increased proliferative response of splenic lymphocytes or cytokine changes was not altered by dexmedetomidine. These data suggest that dexmedetomidine altered NK cell cytotoxic activity, which might have clinical relevance during acute or short treatment periods. Chronic sustained administration should be assessed further in terms of its effects on tumor surveillance and antibacterial activity.
References
- 1.Chapman CR, Tuckett RP, Song CW. Pain and stress in a systems perspective: reciprocal neural, endocrine, and immune interactions. J Pain. 2008;9:122–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2007.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sharify A, Mahmoudi M, Izad MH. et al. Effect of acute pain on splenic NK cell activity, lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production activities. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2007;29:465–76. doi: 10.1080/08923970701619877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Greisen J. Hokland M. Grofte T, et al. Acute pain induces an instant increase in natural killer cell cytotoxicity in humans and this response is abolished by local anesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 1999;83:235–40. doi: 10.1093/bja/83.2.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Flores LR, Dretchen KL, Bayer BM. Potential role of the autonomic nervous system in the immunosuppressive effects of the acute morphine administration. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996;318:437–46. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(96)00788-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Martin E. Ramsay G. Mantz J, et al. The role of the a2-adrenoceptor agonist dexmedetomidine in postsurgical sedation in the intensive care unit. J Intensive Care Med. 2003;18:29–41. doi: 10.1177/0885066602239122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kamibayashi T, Maze M. Clinical uses of alpha 2-adrenergic agonists. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:1345–9. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200011000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Qiao H, Sanders RD, Ma D. et al. Sedation improves early outcome in severely septic Sprague Dawley rats. Crit Care. 2009;13:R136. doi: 10.1186/cc8012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hofer S, Steppan J, Wagner T. et al. Central sympatholytics prolong survival in experimental sepsis. Crit Care. 2009;13:R11. doi: 10.1186/cc7709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Taniguchi T, Kurita A, Kobayashi K. et al. Dose- and time-related effects of dexmedetomidine on mortality and inflammatory responses to endotoxin-induced shock in rats. J Anesth. 2008;22:221–8. doi: 10.1007/s00540-008-0611-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hunskaar S, Hole K. The formalin test in mice: dissociation between inflammatory and non-inflammatory pain. Pain. 1987;30:103–14. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(87)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ishiyama M, Miyazono Y, Sasamoto K. et al. A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability. Talanta. 1997;44:1299–1305. doi: 10.1016/s0039-9140(97)00017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Konjevic´ G, Jurisˇic´ V, Spuzˇic´ I. Correction of the original lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay for the evaluation of NK cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods. 1997;200:199–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(96)00194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Huong PL, Kolk AH, Eggelte TA. et al. Measurement of antigen specific lymphocyte proliferation using 5-bromo-deoxyuridine incorporation: an easy and low cost alternative to radioactive thymidine incorporation. J Immunol Methods. 1991;140:243–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90377-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li X, Eisenach JC. Alpha 2A-adrenoceptor stimulation reduces capsaicin-induced glutamate release from spinal cord synaptosomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;299:939–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Guo TZ, Jiang JY, Buttermann AE. et al. Dexmedetomidine injection into the locus ceruleus produces antinociception. Anesthesiology. 1996;84:873–81. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199604000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Herberman RB, Ortaldo JR. Natural killer cells: their roles in defense against disease. Science. 1981;214:24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Inada T, Shirane A, Hamano N. et al. Effect of subhypnotic doses of dexmedetomidine on antitumor immunity in mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2005;27:357–69. doi: 10.1080/08923970500240883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hamra JG, Yaksh TL. Equianalgesic doses of subcutaneous but not intrathecal morphine alter phenotypic expression of cell surface markers and mitogen-induced proliferation in rat lymphocytes. Anesthesiology. 1996;85:355–65. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199608000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Toge T. Hirai T, Takiyama W, et al. Effects of surgical stress on natural killer activity, proliferative response of spleen cells and cytostatic activity of lung macrophages in rats. Gann. 1981;72:790–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yuki K, Soriano SG, Shimaoka M. Sedative drug modulates T-cell and lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 function. Anesth Analg. 2011;112:830–8. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31820dcabb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sanders RD, Sun P, Patel S. et al. Dexmedetomidine provides cortical neuroprotection: impact on anaesthetic-induced neuroapoptosis in the rat developing brain. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2010;54:710–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2009.02177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sanders RD, Giombini M, Ma D. et al. Dexmedetomidine exerts dose-dependent age-independent antinociception but age-dependent hypnosis in Fischer rats. Anesth Analg. 2005;100:1295–1302. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000149595.41576.B3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Davies MF, Tsui J, Flannery JA. et al. Activation of alpha2 adrenergic receptors suppresses fear conditioning: expression of c-Fos and phosphorylated CREB in mouse amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:229–39. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yeager MP, Procopio MA, DeLeo JA. et al. Intravenous fentanyl increases natural killer cell cytotoxicity and circulating CD16(+) lymphocytes in humans. Anesth Analg. 2002;94:94–9. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200201000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tasdogan M, Memis D, Sut N. et al. Results of a pilot study on the effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine on inflammatory responses and intraabdominal pressure in severe sepsis. J Clin Anesth. 2009;21:394–400. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2008.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vyas D, Javadi P, Dipasco PJ. et al. Early antibiotic administration but not antibody therapy directed against IL-6 improves survival in septic mice predicted to die on basis of high IL-6 levels. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;289:R1048–53. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00312.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wu X, Song X, Li N. et al. Protective effects of dexmedetomidine on blunt chest trauma induced pulmonary contusion in rats. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;74:524–30. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31827d5de3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bekker A, Haile M, Kline R. et al. The effect of intraoperative infusion of dexmedetomidine on the quality of recovery after major spinal surgery. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2013;25:16–24. doi: 10.1097/ANA.0b013e31826318af. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schleifer S.J. Keller S.E. Camerino M. et al. Suppression of lymphocyte simulation after bereavement. J Am Med Assoc. 1983;250:374–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chida Y. Sudo N. Sonoda J. et al. Electric foot shock stressinduced exacerbation of α-galactosylceramide triggered apoptosis in mouse liver. Hepatology. 2004;39:1131–40. doi: 10.1002/hep.20158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lundy J. Ford C.M. Surgery, trauma, and immune suppression. Evolving the mechanism. Ann Surg. 1983;197:434–8. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198304000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]