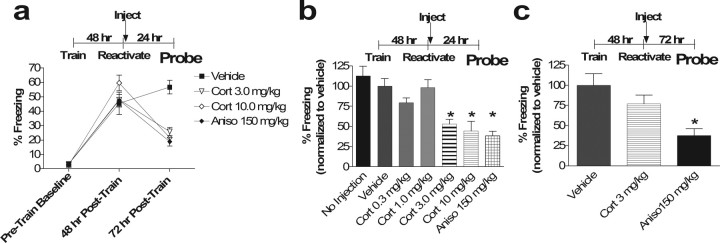
Figure 1.
Postretrieval corticosterone transiently impairs subsequent recall of contextual fear conditioning. a, Percentage of time spent freezing in the training context before training in fear conditioning (Baseline), during subsequent reactivation 48 h hence (48 h from Train), and 24 h after reactivation (72 h from Train). Reactivation was followed by injection of vehicle or corticosterone at the indicated dose (one-way ANOVA for 72 h time point, p < 0.001, F(3,28) = 10.06; post hoc Tukey's test, p < 0.01 for Cort 3 mg/kg vs vehicle, p < 0.001, for Cort 10 mg/kg vs vehicle, p = 0.65, for Cort 3 mg/kg vs Aniso, p = 0.96, for Cort 10 mg/kg vs Aniso, p < 0.001, for Aniso vs vehicle, p = 0.90, for Cort 3 mg/kg vs Cort 10 mg/kg). b, Subsequent contextual memory recall is blocked by higher doses of corticosterone, and this effect resembles that of anisomycin. A dose–response curve for corticosterone administered immediately after memory reactivation is shown. Bars represent percentage of freezing 72 h after training (24 h after memory reactivation) (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.0001, F(6,49) = 10.86; post hoc Tukey's test, vehicle vs no injection, p = 0.95, vs Cort 0.3 mg/kg, p = 0.11, vs Cort 1 mg/kg, p = 0.99, vs Cort 3 mg/kg, p < 0.05, vs Cort 10 mg/kg, p < 0.01, vs Aniso, p < 0.001). No Injection was significantly different from Aniso, Cort 3 mg/kg, and Cort 10 mg/kg (p < 0.001 for all) and not different from Vehicle, Cort 0.3 mg/kg, or Cort 1 mg/kg (p = 0.95, 0.15, and 0.92, respectively). Cort 3 mg/kg differed from vehicle, Cort 1 mg/kg, and No Injection (p < 0.05, 0.05, and 0.01, respectively) but did not differ from Cort 0.3 mg/kg or Aniso (p = 0.39 and 0.92, respectively). Similarly, Cort 10 mg/kg differed from vehicle, Cort 1 mg/kg, and No Injection (p < 0.01, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively) but did not differ from Cort 0.3 mg/kg or Aniso (p = 0.11 and 0.99, respectively). ∗p < 0.05 on post hoc Tukey's test versus vehicle and No Injection. c, Effect of corticosterone on subsequent memory recall is transient. Error bars represent freezing 120 h (5 d) after training (72 h after memory reactivation). When tested 72 h after reactivation, the anisomycin effect on subsequent recall remained, whereas that of corticosterone is no longer present (ANOVA main effect of drug, p < 0.01, F(2,21) = 7.72; post hoc Tukey's test vehicle vs Aniso, ∗p < 0.01, vehicle vs Cort, p = 0.34; Aniso vs Cort, p = 0.058). Although b and c were necessarily performed in separate experiments in different groups on different days and thus normalized to separate control groups, a Student's t test comparison between Cort 3 mg/kg at 24 h from b and Cort 3 mg/kg at 72 h from c revealed a p = 0.068, whereas a similar comparison of Aniso 150 mg/kg at 24 h from b and Aniso 150 mg/kg from c revealed a p = 0.94. n = 8 in all groups. Error bars represent SEM in all figures.