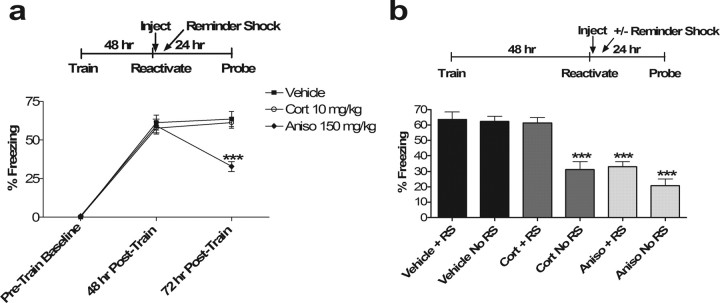
Figure 3.
a, Reminder shock rescues post-reactivation glucocorticoid effect on subsequent memory and spares that of anisomycin. ANOVA at the 72 h time point after reminder shock reveals a main effect of drug (p < 0.00001; F(2,33) = 19.52). Post hoc Tukey's test shows significant differences between vehicle and Aniso and between Cort and Aniso (p < 0.001 for both). There was no significant difference between vehicle and Cort with reminder shock (p = 0.91). ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus corresponding vehicle control. No significant differences were observed in pretrain baseline or 48 h posttrain groups (n = 12 in all groups). b, Comparison of reminder shock (+RS) versus no-reminder shock (no RS) groups on the final day of testing for each drug. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus corresponding vehicle control. Two-way ANOVA: main effect of drug, F(2,66) = 37.25, p < 0.001; main effect of RS/no RS, F(1,66) = 13.76, p < 0.001; interaction, F(2,66) = 5.42, p < 0.01. Post hoc Tukey's test indicated significant differences between Cort/no RS, Aniso/RS, and Aniso/no RS versus all other groups and vice versa; p < 0.001 for all post hoc differences. Nonsignificant p values were 0.36 for Cort/no RS versus Aniso/no RS, 0.47 for Aniso/RS versus Aniso/no RS, 0.99 for Aniso/RS versus Cort/no RS, 0.99 for Cort/RS versus Vehicle/no RS, and 0.99 for Vehicle/RS versus Vehicle/no RS (n = 12 in all groups). No significant differences were observed in pretrain baseline or 48 h posttrain groups.