Figure 2.
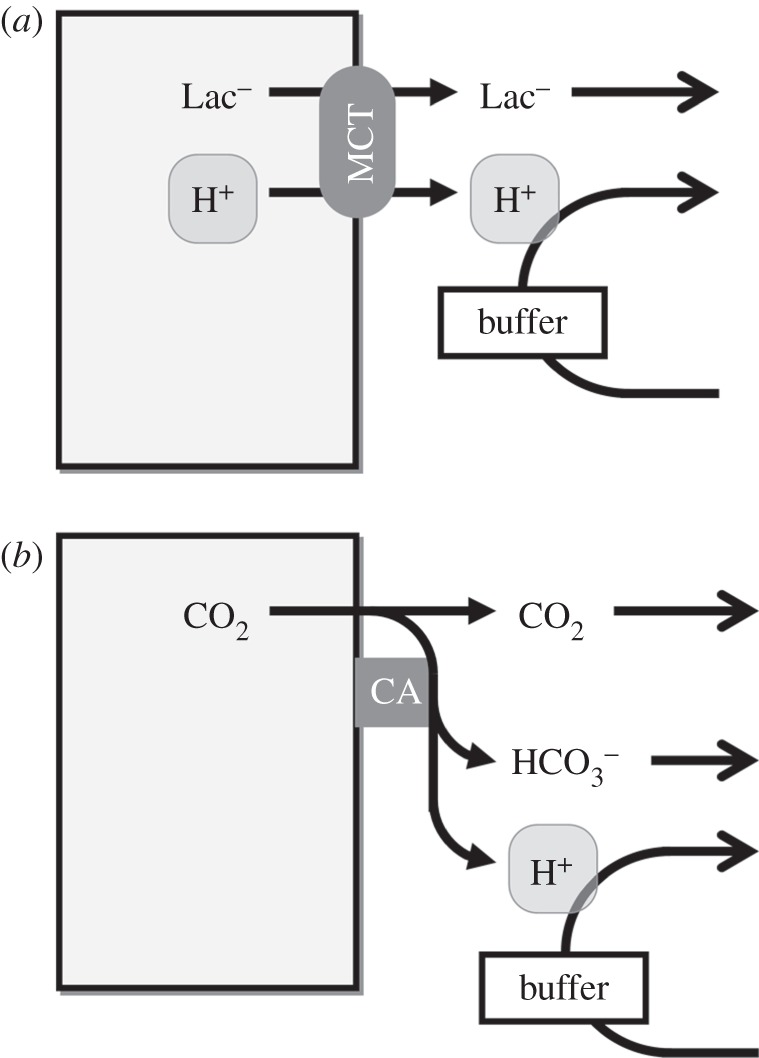
Venting of metabolically produced acids. (a) H+-lactate efflux across the membrane is facilitated by H+-monocarboxylate transport (MCT). Diffusion of H+ and lactate away from the cell-surface is necessary for sustained MCT activity. Mobile H+-buffers can facilitate H+ diffusion and support H+-lactate venting. (b) CO2 can permeate the cell membrane through the lipid bilayer or gas channels. Spontaneous CO2 hydration is slow, but can be accelerated by exo-facial carbonic anhydrase (CA) enzymes. Diffusion of the hydration products alongside CO2 represents a form of facilitated CO2 diffusion.
