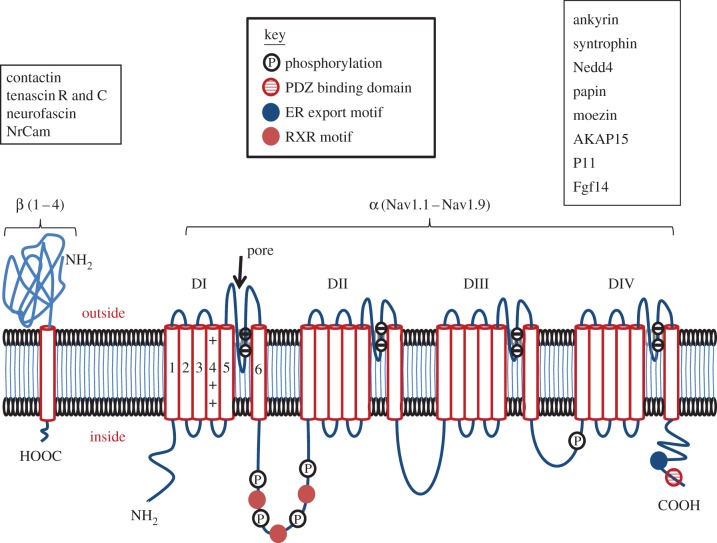
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the structure and membrane topology of the voltage-gated sodium channel showing the main regulatory sites. Given α-subunits have four domains (DI–DIV) each composed of six transmembrane segments. Within the latter, segment four contains positively charged amino acids and this is the main voltage-sensitive region; the loop between transmembrane segments 5 and 6 is negatively charged and forms the pore region. Many types of modulatory sites exist for both α- and β-subunits as indicated by the key. The boxes adjacent to α- and β-subunits list the proteins known to interact with each subunit, respectively. PDZ, post-synaptic density protein (PSD95) and Drosophila disc large tumour suppressor (Dlg1) and zonula occludens-1 protein (zo-1); ER, endoplasmic reticulum; RXR, a motif which mediates retention of proteins in the ER. (Online version in colour.)