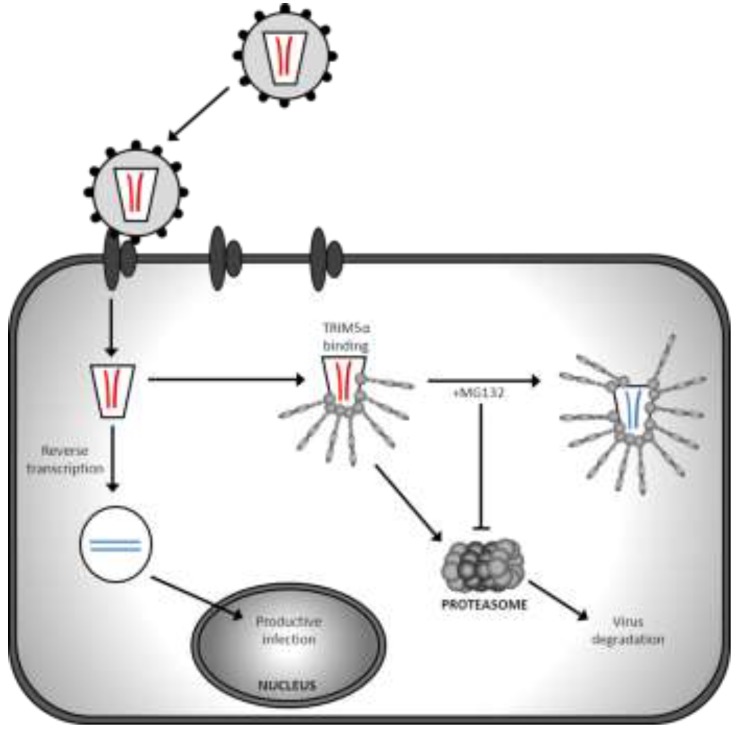
Figure 2.
Schematic showing TRIM5α restriction of virus within a cell. TRIM5α is autoubiquitinylated by its RING domain and when virus enters the cell TRIM5α binds viral capsid via its B30.2 domain, targeting the virus for proteasomal degradation. This block to infection occurs prior to reverse transcription. If cells are treated with MG132 to inhibit the proteasome, reverse transcription occurs and the virus is not degraded, but infection is not rescued. This suggests alternative proteasomal independent antiviral mechanisms.