Figure 3.
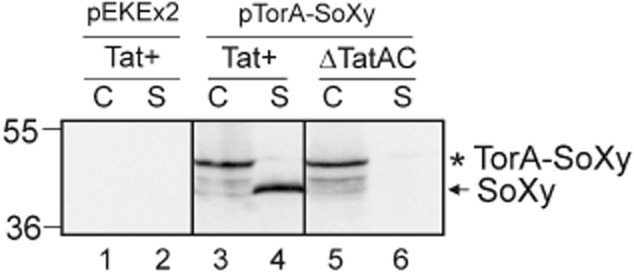
Transport of TorA–SoXy occurs in a strictly Tat-dependent manner. Plasmid pTorA–SoXy was transformed into C. glutamcium ATCC13032 (Tat+) and a C. glutamicum ΔTatAC mutant that lacks a functional Tat translocase (Meissner et al., 2007). As a control, the empty pEKEx2 expression vector was transformed into C. glutamicum ATCC13032 (Tat+). The respective strains were grown overnight in 5 ml of BHI medium (Difco) at 30°C. The cells were washed once with BHI and resuspended in 20 ml of fresh BHI medium containing 1 mM IPTG. After 6 h of further growth at 30°C, the cellular (C) and supernatant (S) fractions were prepared as described previously (Meissner et al., 2007). Samples of the C and S fractions were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting using anti-SoXy antibodies as indicated at the top of the figure. Lanes 1 and 2: C. glutamicum ATCC13032 (pEKEx2); lanes 3 and 4: C. glutamicum ATCC13032 (pTorA–SoXy); lanes 5 and 6: C. glutamicum ΔTatAC (pTorA–SoXy). Asterisk: TorA–SoXy precursor; arrow: secreted SoXy protein. The positions of molecular mass markers (kDa) are indicated at the left margin of the figure.
