Fig. 2.
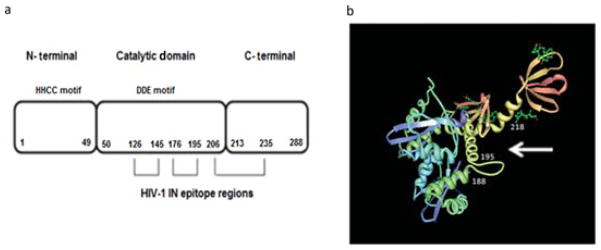
Schematic representation of HIV-1 IN and its interactions with anti-IN–scFvs. (a) Linear model of HIV-1 IN protein and the domains recognized by anti-IN–scFv clones 7, 104, 135, 142, and 144. The IN enzyme is composed of the N-terminal domain (NTD, aa 1–49), catalytic core domain (CCD, aa 50–212), and C-terminal domain (CTD, aa 213–288). The H and C residues within the NTD are conserved among retrotransposon integrase proteins. The D and E residues in the CCD form the DDE motif. All anti-IN–scFvs tested recognized and bound to residues 126–145 (peptide 4,338), residues 176–195 (peptide 4,343), and to the upstream residues 206–235 (peptides 4,346 and 4,347). (b) Model of the crystal structure of HIV-1 catalytic and C-terminal domains (PDB code 1EX4) [63] showing the epitopes recognized by the anti-IN–scFvs. The probable binding site of scFvs to HIV-1 IN is indicated by a white arrow.
