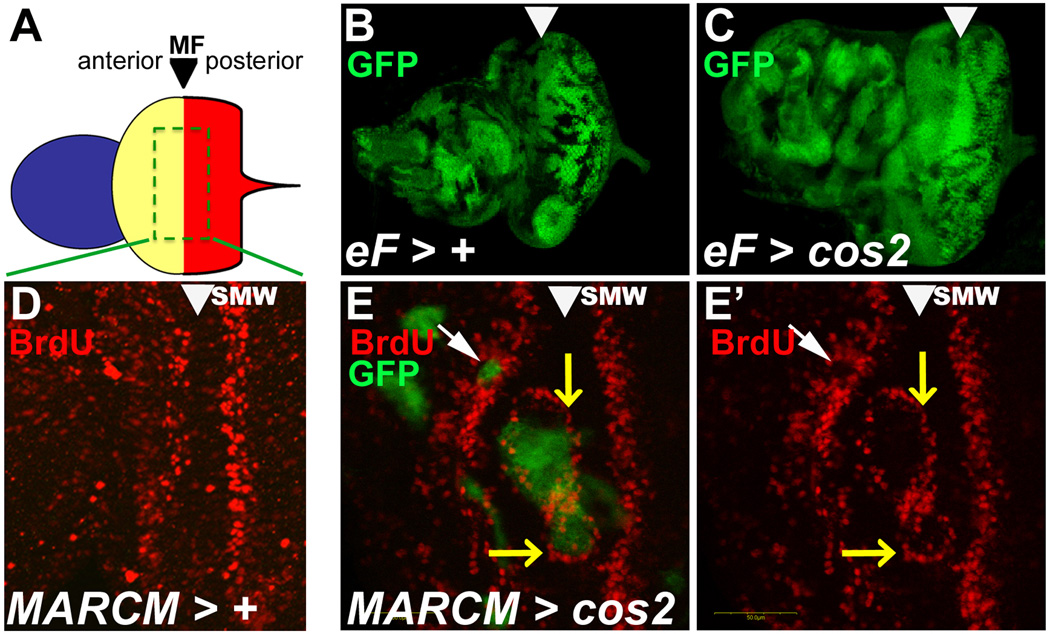
Figure 2. Ectopic proliferation in cos2 mosaics eye disc at or anterior to the MF.
Shown are eye-antennal imaginal discs from 3rd instar larvae. The MF is marked by arrowheads. Clones were induced by ey-FLP (eF) induced mitotic recombination, symbolized by >.
(A) Schematic view of the eye-antennal disc. Anterior (blue) forms the antenna. Central (yellow) forms the head capsule, and posterior (red) forms the eye field which are separated by the morphogenetic furrow (MF).
(B,C) Size comparison of age-matched control (B) and cos2 mosaic discs (C). Although mutant clones (marked by the absence of GFP) are smaller in cos2 mosaics, the mosaic discs are larger and often deformed compared to control discs.
(D) The normal BrdU pattern in wild-type discs. SMW – second mitotic wave.
(E,E’) cos2 clones, positively marked by GFP due to MARCM, located in the MF stimulate BrdU incorporation at the boundary of the clone (white arrowhead). Clones anterior to the MF (yellow arrow) have reduced BrdU labeling.
- (B) y w ey-FLP; FRT42 ubi-GFP/FRT42
- (C) y w ey-FLP; FRT42 ubi-GFP/FRT42 cos2H29
- (D) y w hs-FLP UAS-mCD8-GFP; FRT42 cos2H29 /CyO; tubP[GAL4]/+
- (E,E’) y w hs-FLP UAS-mCD8-GFP; FRT42 tubP[GAL80]/FRT42 cos2H29 ; tubP[GAL4]/+