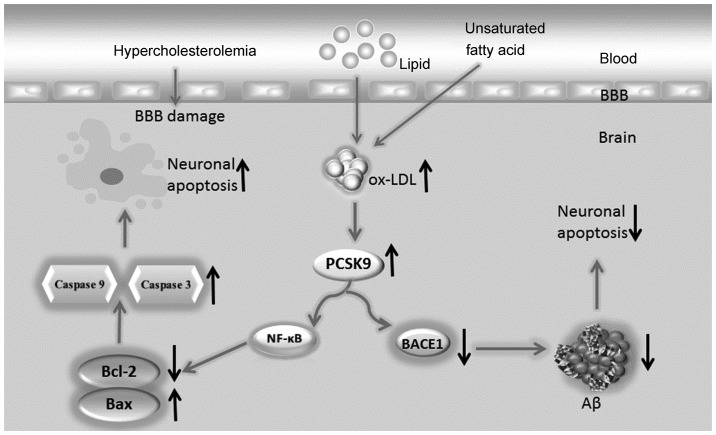
Figure 1.
Dual regulatory effect of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) on neuronal apoptosis. Hyperlipidemia increases the lipid content in the brain, particularly oxidized LDL (ox-LDL). High ox-LDL levels may upregulate the PCSK9 expression in neurons. Neuronal apoptosis is induced through the NF-κB-Bcl-2/Bax-caspase 9-caspase 3 signaling pathway when PCSK9 expression increases. Additionally, through BACE1 degradation, PCSK9 may reduce amyloid β peptide (Aβ) generation by inhibiting the amyloid precursor protein/Aβ metabolic pathway, thereby decreasing neuronal apoptosis induced by Aβ.