Figure 2.
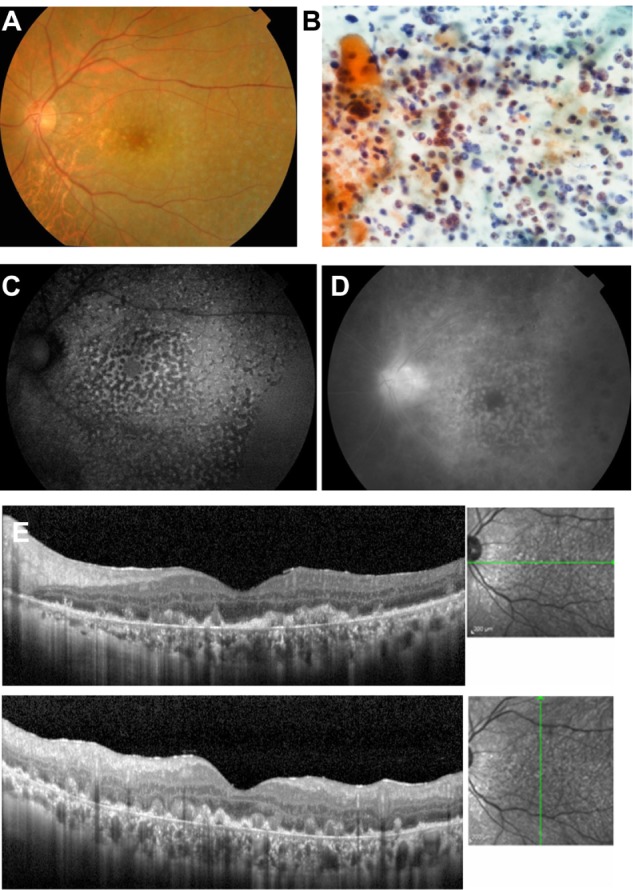
Case 2. Fundus images of the left eye in a 57-year-old man with primary intraocular lymphoma after vitrectomy.
Notes: (A) Color fundus photograph shows many small, yellowish lesions with distinct boundaries resembling drusen in the posterior fundus. (B) Cytological examination of vitrectomy specimen shows atypical lymphocytes with dyskaryosis and aberrant chromatin, stained using May-Grünwald-Giemsa. (C) Granular pattern of hypoautofluorescence and hyperautofluorescence is seen on fundus autofluorescence. (D) Late phase of fluorescein angiography shows hyperfluorescence of the disc and small spots with a reverse fluorescence pattern to the fundus autofluorescence pattern. (E) Spectral-domain optical coherence tomographic images. Nodular hyper-reflective infiltration at the level of retinal pigment epithelium and above the retinal pigment epithelium, a separation of Bruch’s membrane from the retinal pigment epithelium, partial destruction of the retinal pigment epithelium, disruption of the photoreceptor inner segment/outer segment junction line, and multiple hyper-reflective signals in the inner retina can be seen.
