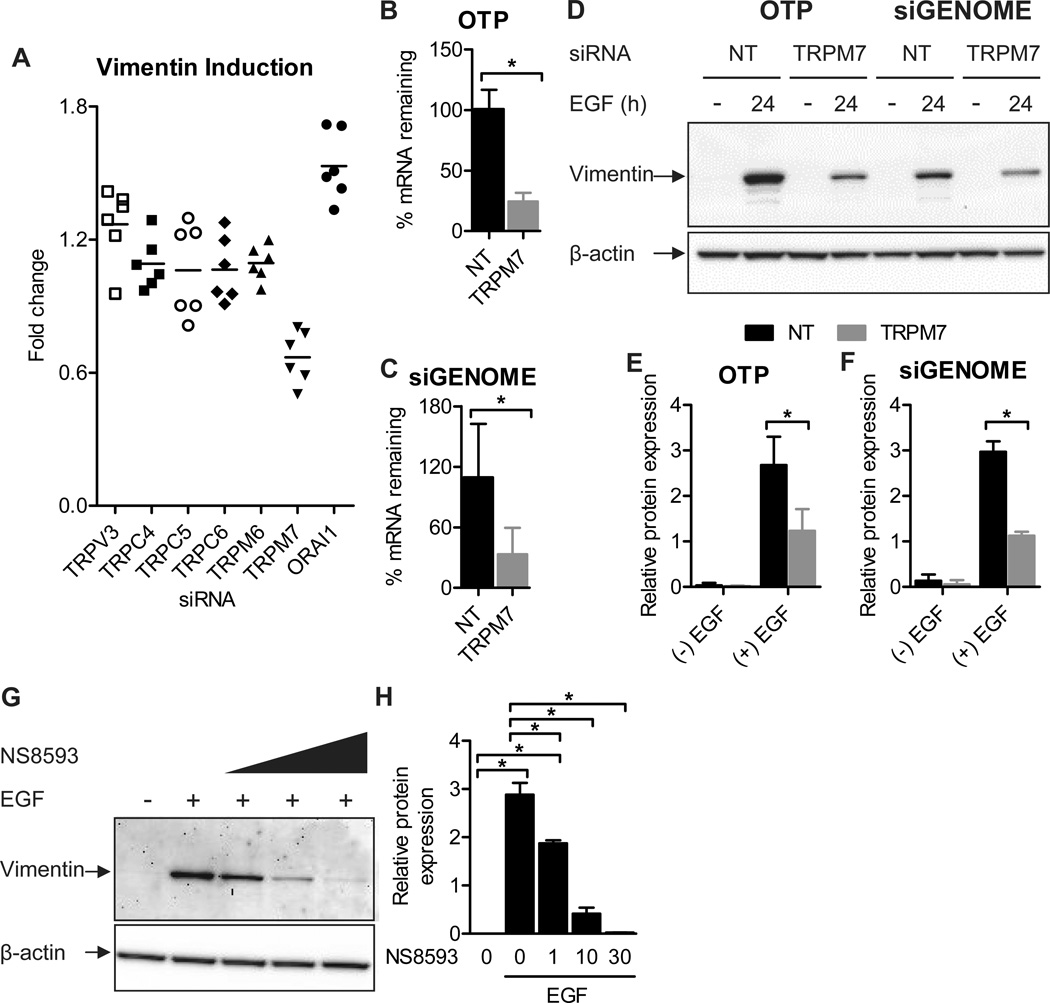
Figure 6. siRNA silencing and pharmacological inhibition of TRPM7 inhibit EGF-induced vimentin protein expression.
A) TRPV3, TRPC4, TRPC5, TRPC6, TRPM6, TRPM7 and ORAI1 calcium-permeable channels were silenced using Dharmacon ON-TARGETplus siRNA and cells were stimulated with EGF (10 ng/mL, 24 h). Vimentin protein expression (integrated intensity) was assessed with quantitative immunofluorescence. The scatter dot plot shows fold change relative to the non-targeting (NT) control for six individual wells from two independent experiments. Analysis of percent TRPM7 mRNA remaining following transfection with B) Dharmacon ON-TARGETplus (OTP) TRPM7 siRNA or C) Dharmacon siGENOME TRPM7 siRNA. Bar graphs show mean ± S.D. for six wells from two independent experiments. Statistical significance was assessed using a student’s t-test. D) Representative immunoblot confirming regulation by TRPM7 of EGF-induced vimentin expression and densitometric analysis of vimentin expression (normalized to β-actin) in cells transfected with E) OTP TRPM7 siRNA or F) siGENOME TRPM7 siRNA. Graphs show mean ± S.D. for three independent experiments. The effect of TRPM7 gene silencing on vimentin expression was assessed using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons post-tests. G) Representative immunoblot showing the effect of increasing concentrations of the TRPM7 inhibitor NS8593 on EGF-induced vimentin expression and H) densitometric analysis (normalized to β-actin) for three independent experiments. Cells were treated with NS8593 for 24 h prior to EGF treatment and NS8593 was maintained during EGF treatment. Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons post-tests. * P < 0.05.