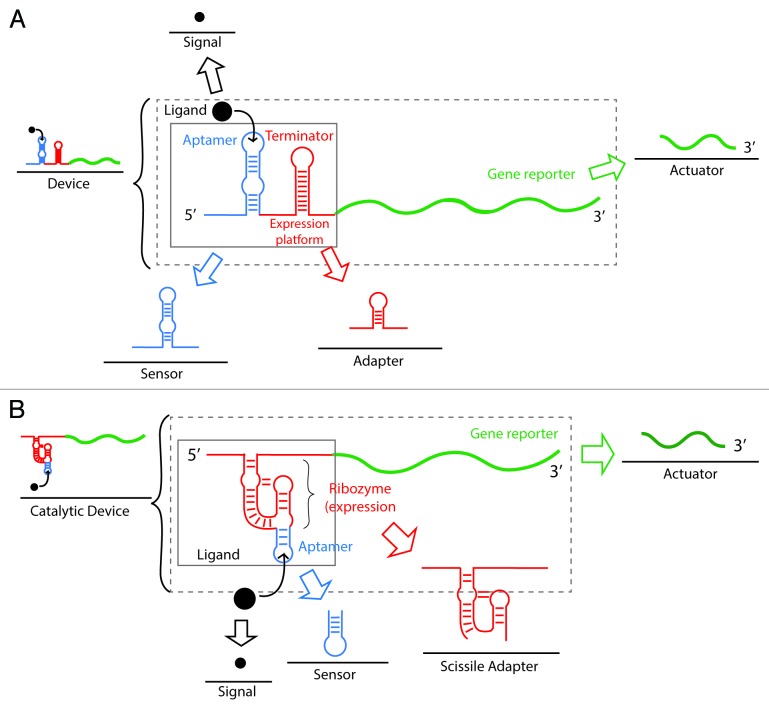
Figure 4. Composability of riboswitches as a strategy for the synthesis of artificial RNA devices. Composability refers to the ability of a system to break down in units (parts) due to the system modularity and recombine in different configurations to satisfy specific human requirements. (A) Composability of riboswitches. Riboswitches can be decomposed and recombined for the synthesis of new devices with high modularity. An artificial riboswitch-based device is composed of a regulator (riboswitch), a signal (ligand), and an actuator (gene reporter). The regulator (inside the solid square) can be further decomposed into a sensor (aptamer) and an adaptor (expression platform that usually contains a terminator stem). (B) Composability of aptazymes (allosteric ribozymes). A synthetic catalytic device is composed of a catalytic regulator (aptazyme), a signal (ligand), and an actuator (gene reporter). The catalytic regulator (inside the solid box) can be further disassembled in a sensor (aptamer) and a scissile adaptor (ribozyme).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.