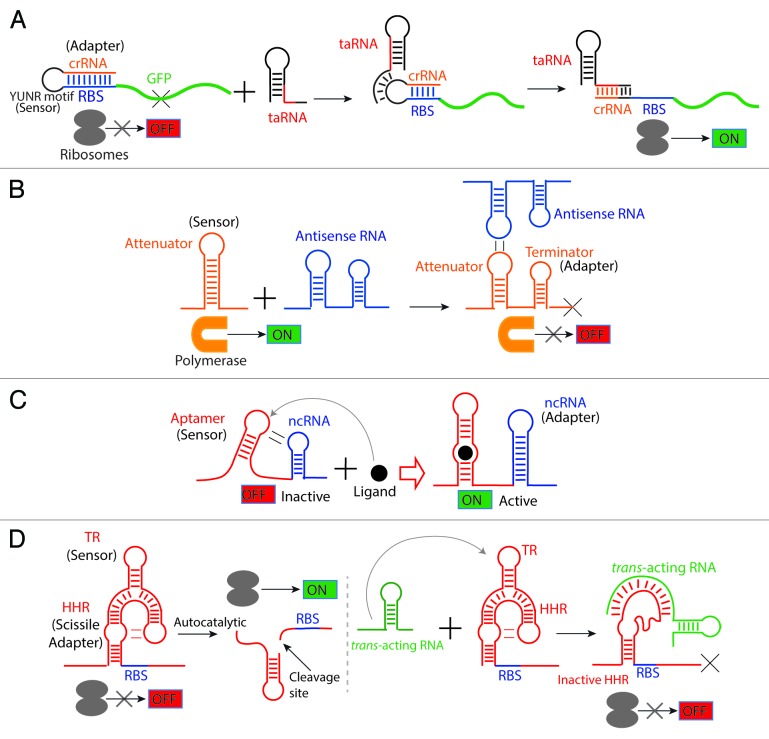
Figure 6. Dual and chimeric riboregulators. Based on the composability of these regulatory molecules, they can be recombined and assembled into a new regulator that exerts a completely different function. (A) Translational control by a small trans-acting RNA-responsive switch. Isaacs and collaborators designed a riboregulator combining a riboswitch-like sensor (YUNR motif), an adaptor that contains an anti-RBS sequence (crRNA) that can pair with the RBS and an sRNA-like effector molecule (taRNA). Translation is OFF (left) when the taRNA absent since crRNA sequesters the Ribosomal Binding Site (RBS). Translation turns ON (right) in the presence of the taRNA since it releases the RBS by recognizing the YUNR motif120 that leads to disruption of the CrRNA-RBS stem-loop.73 (B) Transcriptional control by a small trans-acting RNA-responsive switch. A transcriptional attenuator (from plasmid pT181) was engineered to be RNA sensitive. The sensor loop in the attenuator was evolved to detect a short antisense RNA (that acts as an effector molecule) via a kissing-loop interaction. This interaction exposes an intrinsic transcriptional terminator (the adaptor) to turn transcription OFF.74 (C) A ligand-responsive riboswitch activating an ncRNA. A chimeric regulator was engineered by using a natural aptamer as sensor and a non-coding antisense RNA (ncRNA) as the adaptor. By means of a kissing-loop interaction in the absence of the ligand, the aptamer interacts with the ncRNA hairpin inactivating its antisense function. In the presence of the ligand, the hairpin interaction is disrupted and the ncRNA recovers its regulatory functions.75 (D) An sRNA-responsive aptazyme. A trans-acting RNA-sensitive hallosteric ribozyme was engineered by designing a sensor (TR: trans-acting RNA responsive element) that detects the trans-acting RNA and coupling it with a Hammerhead ribozyme (HHR). In the absence of the trans-acting RNA (left), the aptazyme undergoes cleavage exposing the (initially occluded) ribosomal binding site and allowing translation. In contrast, upon binding of the trans-acting RNA to the TR element, the Hammerhead ribozyme undergoes a structural change that renders it catalytically inactive; this masks the RBS and prevents translation initiation.76

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.