Fig 1.
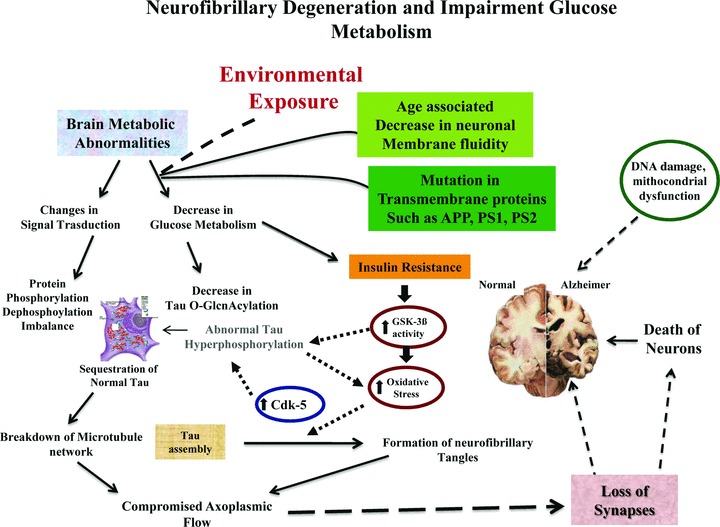
Protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation imbalance is generated, at least in part, by a decrease in the activities of τ phosphatases and increase the activities of τ kinase (i.e. cdk5, GSK-3, etc.) affected by insulin. Impaired insulin signalling stimulates GSK-3β activity that increases oxidative stress and τ hyper-phosphorylation, by Cdk-5. Severe or sustained oxidative injury leads to mithocondrial DNA damage, mithocondrial dysfunction, apoptosis and the attendant cell loss and impaired neuronal function lead to dementia. Age reduces membrane fluidity inducing mutations in transmembrane proteins (i.e. PS1, PS2, APP), and vulnerability of the cell membrane to variation in pathological signal transduction.
