Fig 2.
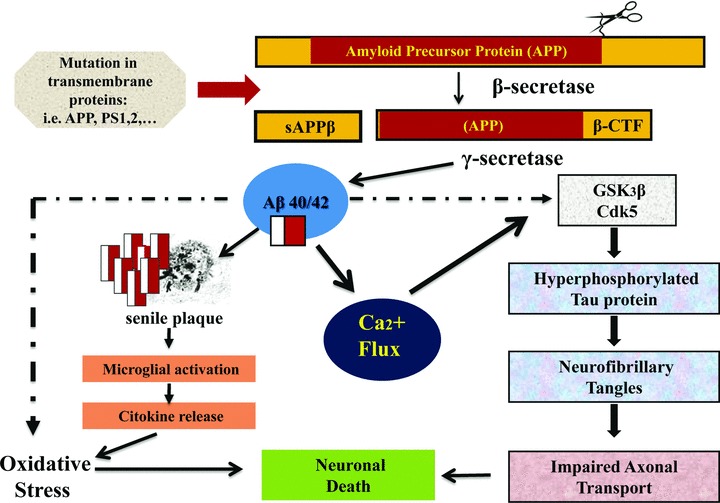
Aβ is a small peptide with N- and C-terminal heterogeneity, that is Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42, which are released from a transmembrane glycoprotein, the amyloid precursor protein (APP) via sequential cleavage by aspartyl proteases: the β and γ secretases. Aβ/40/42 activates Ca2+ influx in neurons, hyperphosphorilation of τ protein (via activation of GSK3β and CDK5), leading to oxidative stress, deposition of neurofibrillary tangles, impaired axonal transport and, finally, to neuronal death.
