Fig 4.
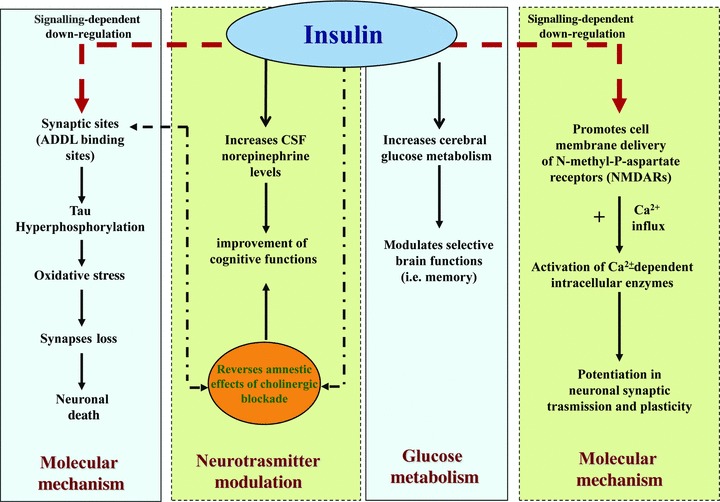
(1) Molecular mechanism insulin promotes cell membrane expression of NMDA receptors, which increases neuronal Ca2− influx-dependent enzymes and strengthens neuronal synaptic association. Besides, diffusible ligands (ADDL) binding to particular synaptic sites and the resulting oxidative stress and synapse loss are markedly decreased by the presence of insulin. This mechanism is associated with a signal-dependent down-regulation of ADDL-binding sites. (2) Glucose metabolism low concentrations of exogenous insulin may increase cerebral glucose metabolism and then modulate brain functions, such as memory. (3) Neurotransmitter modulation insulin increases CSF levels of norepinephrine and reverses the amnestics effects of cholinergic blockade.
