Fig 2.
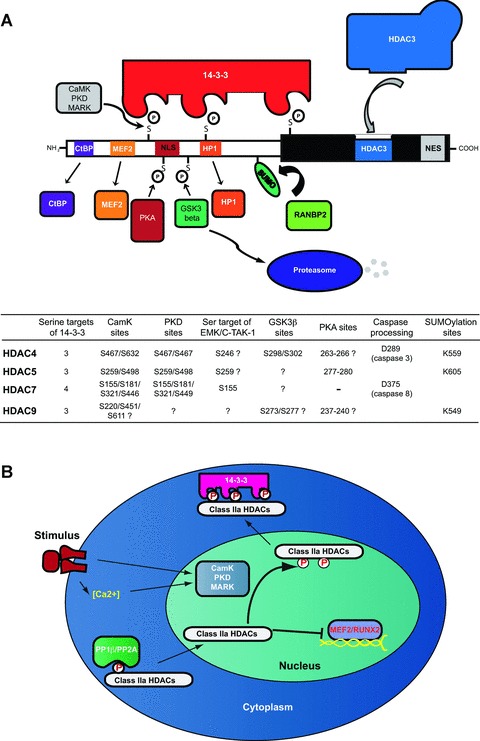
Class IIa HDACs domain organization and shuttling regulation. (A) The amino-terminal domain is subjected to different post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation, sumoylation and caspase cleavage. CaMK, PDK and MARK kinases phosphorylate several Ser residues in the amino-terminal domain thereby promoting the association with 14-3-3 proteins. Additional kinases such as PKA and GSKβ affect class IIa HDACs stimulating nuclear retention and protein degradation respectively. Different interactors associate with the N-terminal domain of class IIa HDACs such as CtBP, MEF2 or HP1, whereas the C-terminal domain can recruit HDAC3-NCoR/SMRT complex to promote Lys deacetylation. In the chart are reported aminoacidic residues involved in several post-translational processes including phosphorylation, sumoylation, caspase processing. (B) Extracellular stimuli that are able to activate CaMK, PDK and MARK kinases trigger the phosphorylation of class IIa HDACs and their association with 14-3-3 proteins, thereby promoting nuclear export. Conversely, the removal of the phosphate groups catalysed by PP1 or PP2A stimulates class IIa HDACs nuclear accumulation and repression of MEF2-dependent gene expression.
