Fig 4.
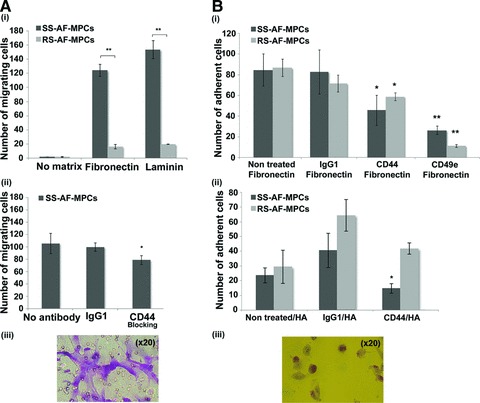
Migration and adhesion properties of SS-AF-MPCs and RS-AF-MPCs. (A) (i) SS-AF-MPCs showed higher motility (**P < 0.001) on fibronectin and laminin, respectively compared to RS-AF-MPCs. (ii) Number of migrated SS-AF-MPCs to fibronectin in presence of CD44 neutralizing antibody or isotype matched non-specific antibody IgG1. (iii) Representative image (20×) of migrated SS-AF-MPCs fixed and stained using the Ral staining kit on the transwell membrane. (B) (i) Number of adherent SS-AF-MPCs and RS-AF-MPCs to fibronectin, treated with CD44, CD49e neutralizing antibodies or isotype matched non-specific antibody IgG1 in comparison to non treated SS-AF-MPCs and RS-AF-MPCs, respectively. (ii) Number of adherent SS-AF-MPCs and RS-AF-MPCs to hyalouronic acid, treated with CD44 neutralizing antibody or isotype matched non-specific antibody IgG1 in comparison to non treated SS-AF-MPCs and RS-AF-MPCs, respectively. (iii) Representative image (20×) of adherent cells fixed and stained using the Ral staining kit on the plastic vessel. Values are shown as mean ± S.D. for three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was carried out using the Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.001).
