2.
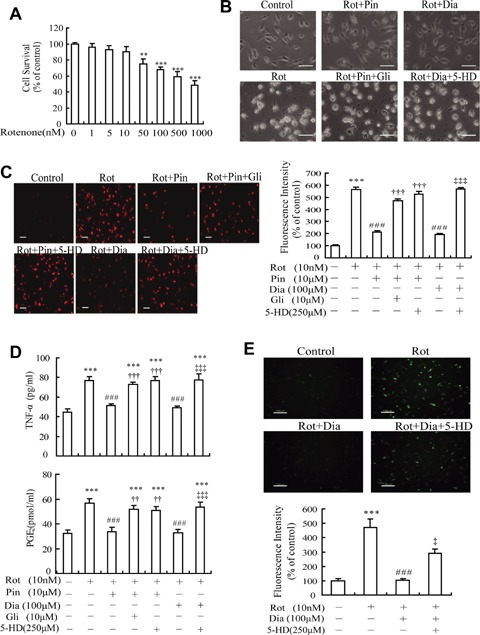
Effects of KATP channel openers on rotenone-induced microglial activation and production of pro-inflammatory and neurotoxic factors. (A) Rotenone induced a decrease in the viability of microglia in a concentration-dependent manner. (B) KATP channel openers attenuated rotenone-induced morphological change of microglia. Rot, rotenone; Pin, pinacidil; Dia, diazoxide; Gli, glibenclamide; 5-HD, 5-hydroxydecanoate. (C) KATP channel openers reduced fluorescence intensity of rotenone-induced ED1-positive microglia (red). (D) KATP channel openers inhibited rotenone-induced production of TNF-α and PGE2 from microglia. (E) KATP channel openers inhibited rotenone-induced production of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in microglia. Scale bar: 50 μm (B and C); 100 μm (E). **P<0.01, ***P <0.001 versus control group; ###P <0.001 versus Rot group; ††P <0.01, †††P <0.001 versus Rot + Pin group; ‡P <0.05, ‡‡‡P <0.001 versus Rot + Dia group. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M. of four independent experiments.
