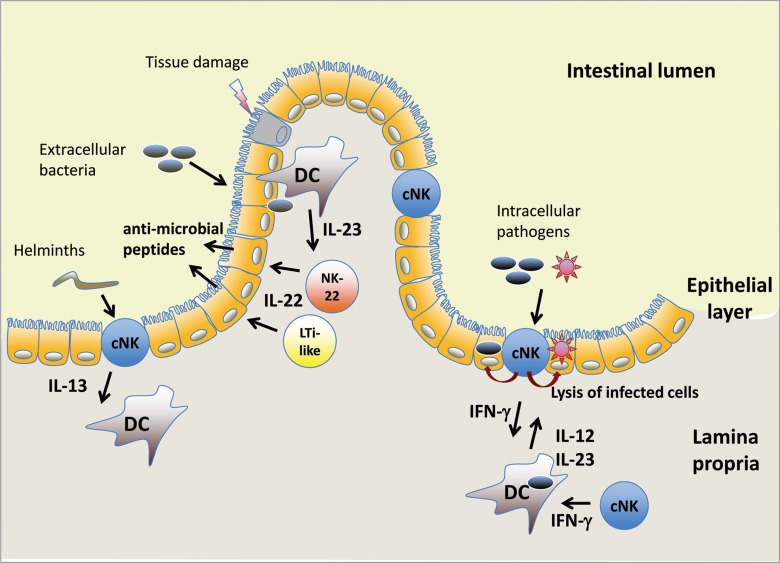
Fig. 1.
cNK cells and NK-22 cells in the intestinal mucosa. cNK cells are found in the intestinal epithelium and in the underlying lamina propria, while NK-22 cells and LTi-like cells reside in the lamina propria. Exposure of dendritic cells (DC) to pathogens triggers the release of IL-12 and/or IL-23, which induces IL-22 secretion by NK-22 and LTi-like cells and IFN-γ secretion by cNK cells. Helminth infections have been shown to cause IL-13 production by intraepithelial NK cells. DC, dendritic cell; cNK, conventional NK cell; LTi-like, adult equivalent of fetal lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi) cells