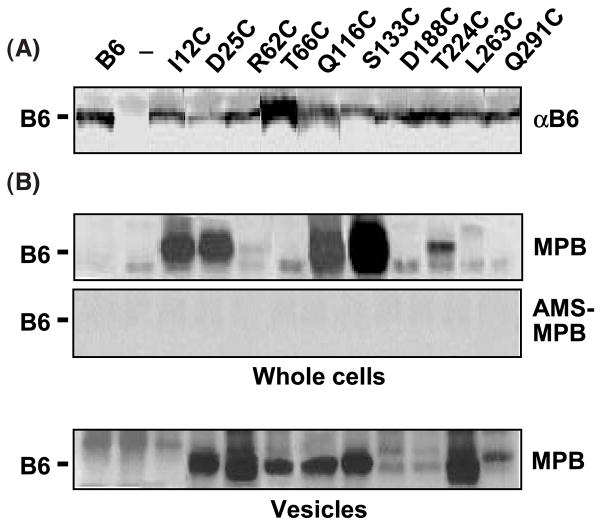
Figure 3.
Accessibility of introduced cysteine residues. Immunodetection of native VirB6 and Cys substitution mutant proteins. Lanes 1, strain PC1006(pSJB964) producing native VirB6 from PvirB-virB6; lanes 2 (—), strain PC1006 (ΔvirB6); and lanes 3 through 12, PC1006 producing the VirB6 Cys substitution mutants listed. Membrane proteins (5 μg) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis with anti-VirB6 antibodies (αB6). MPB labeling of VirB6 Cys substitution mutants. Whole cells: PC1006 (ΔvirB6) strains treated with MPB without (above) or with (below) pretreatment with AMS. Native and mutant forms of VirB6 were isolated by immunoprecipitation and analyzed for MPB labeling as described in Materials and Methods. Vesicles: solvent-accessible Cys residues, as shown by treatment of A. tumefaciens vesicles with MBP. The treatment of whole cells or of vesicles with MPB did not label the unique Cys42 residue of the native protein (B6). Note that MPB labeled a non-VirB6 species migrating slightly faster (whole cells) or slower (vesicles) than VirB6 in the protein gels; these species were labeled in strains producing and lacking VirB6, e.g. ΔvirB6, lane 2.