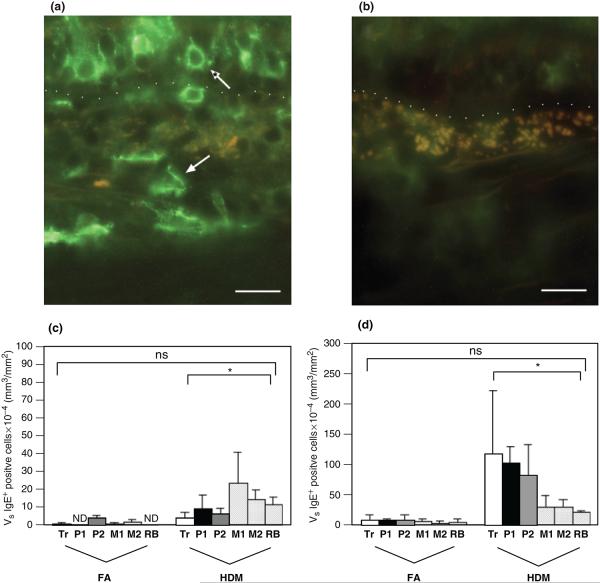
Fig. 3.
Distribution of IgE+ cells within airway mucosa of HDM-challenged rhesus monkeys. IgE+ cells were quantitated by immunofluorescence staining of trachea and left caudal lobe sections obtained from HDM-challenged monkeys. Tr, P1, P2, M1, M2, and RB represent cryosections obtained from tissue blocks of trachea and regions progressively representing the most proximal (P1) to distal (RB) intrapulmonary airways of the lobe. Columns represent the average volume ± SE of IgE+ staining cells (mm3) within the specified compartment with respect to the surface area of basal lamina (mm2). FA, filtered air control; HDM, house dust mite-challenged; RB, respiratory bronchiole. (a) IgE+ immunofluorescence staining of an intrapulmonary airway (block P2) from a representative HDM-challenged monkey. The dotted line defines the basement membrane; the epithelium is above the line, and the interstitium is below the line. The normal arrow points to an interstitial IgE+ cell; the *arrow points to an epithelial IgE+ cell. Bar=20 μm. (b) Control staining of an adjacent section using non-specific goat IgG and ALEXA 488 secondary antibody. Bar=20 μm. (c) Abundance of IgE+ cells within the epithelial compartment of conducting airways. *P=0.0088 by analysis of variance (treatment effect). (d) Abundance of IgE+ cells within the interstitial compartment of conducting airways. *P=0.0125 by analysis of variance (treatment effect).