Fig. 1.
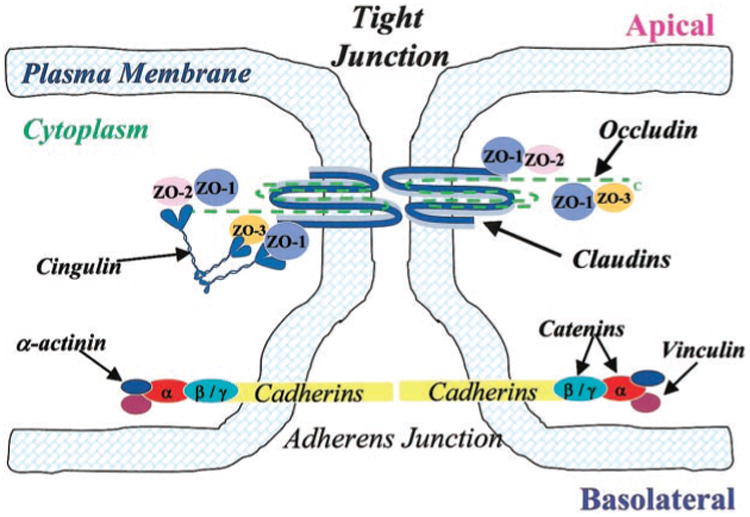
Schematic drawing of proposed junctional architecture of cerebromicrovessel endothelial cells. Tight junctions (TJ) consisting of the integral membrane proteins occludin and claudin are located towards the apical side of endothelial cells with their corresponding cytoplasmic accessory proteins [i.e., zonula occluden (ZO)-1, ZO-2, ZO-3, and cingulin] connecting TJs to the cytoskeleton (i.e., actin; not shown). Adherens junctions (AJ), located toward the basolateral side of endothelial cells, are composed of the integral membrane bound cadherins and cytoplasmic accessory proteins (i.e., α-and β-catenin).
