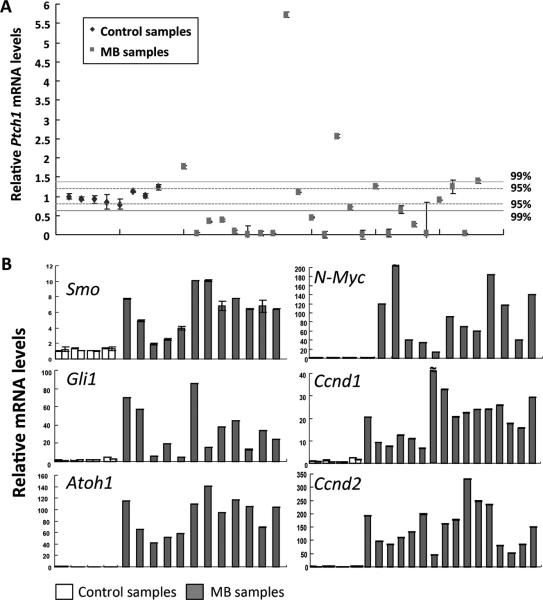
Fig. 3. Dysregulation of the sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway in medulloblastomas.
The qPCR analyses were used to measure the relative level of mRNA in medulloblastoma tissues derived from BCCIP-CKD;p53LoxP/LoxP mice. The mRNA levels of age-matched control (3-months old) cerebellums were also measured. Panel A shows the relative level of Ptch1 mRNA in 24 medulloblastoma samples. Control samples are (from left to right): BCCIP-CON (LoxPshBCCIP+/−; p53wt/wt;GFAP-Cre−/−)(first 2 control data points from the left, n=2), BCCIP-CKD (LoxPshBCCIP+/−; p53wt/wt;GFAP-Cre+/− )(control data points 3 and 4 from the left, n=2), GFAP-Cre (LoxPshBCCIP−/−; p53wt/wt;GFAP-Cre+/−) (n=2) and BCCIP-CON;p53LoxP/LoxP (LoxPshBCCIP−/−; p53LoxP/LoxP;GFAPCre+/− )(n=2). The average of Ptch1 mRNA level and its standard deviation were calculated from control samples. Based on the normal distribution, the 95% confidence limit (p<0.05) was set at 1.96 fold of the standard deviation, and the 99% confidence limit (p<0.01) was set at 2.58 fold of the standard deviation. The 95% and 99% confidence ranges are marked in the graph. A total of 16 cases displayed reduction of Ptch1 mRNA levels. Panel B shows the wide range of mRNA up-regulation of key components of the Shh pathway as indicated in the specific panels. A total of 12 MB samples were analyzed in Smo, Gli1, Atoch1, N-Myc and 16 MB samples were analyzed in Ccnd1 and Ccnd2.