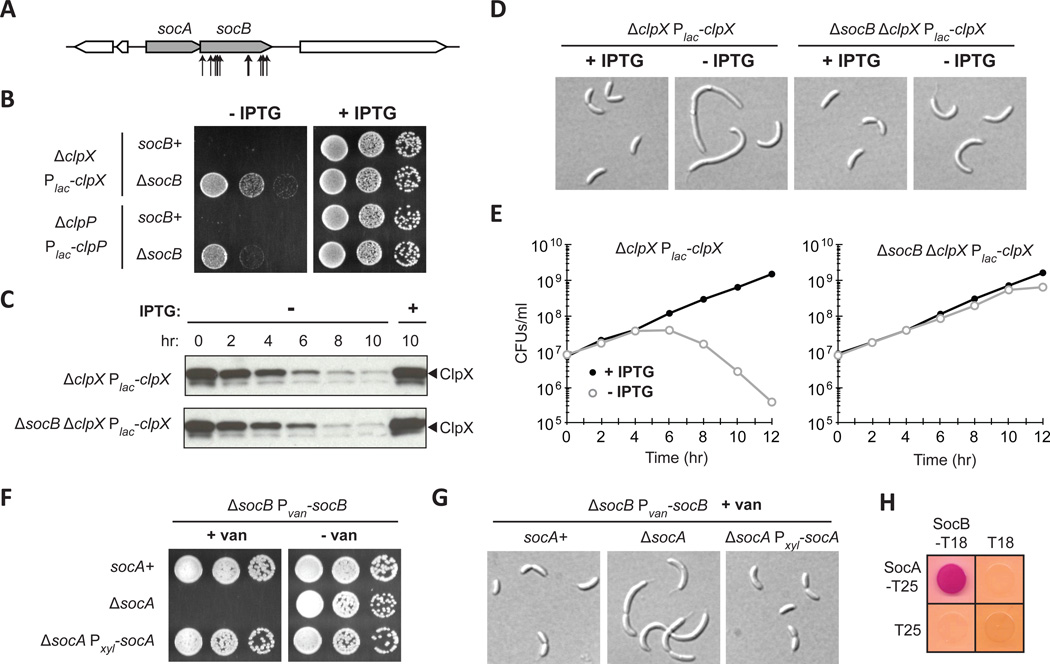
Fig. 1. Mutations in the Toxin socB Bypass ClpXP Essentiality.
(A) Schematic of transposon insertions in socB (CCNA_03629) that suppressed the essentiality of clpP.
(B) Growth of clpX and clpP depletion strains in socB+ and ΔsocB backgrounds. Five-fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains were spotted onto media ± IPTG.
(C) Kinetics of ClpX depletion. Indicated strains were shifted to media ± IPTG, and samples were subjected to immunoblotting.
(D) Morphology of cells following ClpX depletion in socB+ and ΔsocB backgrounds. Strains from (C) were imaged by DIC microscopy at 10 hr.
(E) Viability of cells following ClpX depletion in socB+ and ΔsocB backgrounds. Colony forming units (CFUs)/ml of the strains from (C) are shown; mean of two biological replicates.
(F) Growth of strains expressing socB in the socA+ or ΔsocA backgrounds. The indicated strains were five-fold serially diluted onto media that induces or represses socB.
(G) Morphology of strains from (F). The indicated strains were grown for 4 hr in socB inducing conditions and then imaged by DIC microscopy.
(H) Bacterial two-hybrid analysis of the interaction between SocA and SocB. T18/T25 were included as a negative control; red indicates a positive interaction. Cells were grown for 1 day at 30°C.
See also Fig. S1.