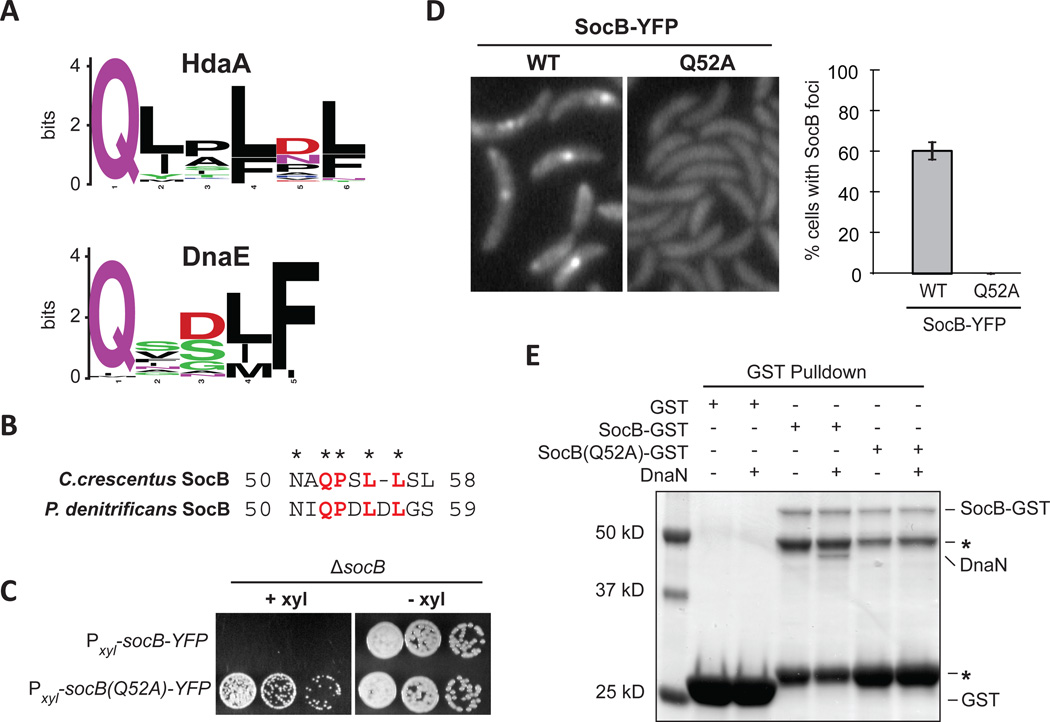
Fig. 6. SocB Interacts with DnaN Through a Conserved Motif.
(A) Sequence logo of the DnaN-binding motif in HdaA or DnaE from α-proteobacteria.
(B) Putative DnaN-binding motif in SocB from C. crescentus and P. denitrificans.
(C) Growth of indicated strains on media that induces (+xyl) or represses (−xyl) socB-YFP or socB(Q52A)-YFP expression. Five-fold serial dilutions are shown.
(D) Fluorescence microscopy of socB-YFP or socB(Q52A)-YFP 3 hr post induction. Percentage of cells with SocB-YFP foci ± S.D. for three biological replicates is shown on right (n>500 cells per replicate).
(E) Interaction between SocB-GST, SocB(Q52A)-GST, and DnaN. Performed as in Fig. 3H; as before, asterisk indicates SocB-GST N-terminal degradation products.
See also Fig. S5.