Figure 1.
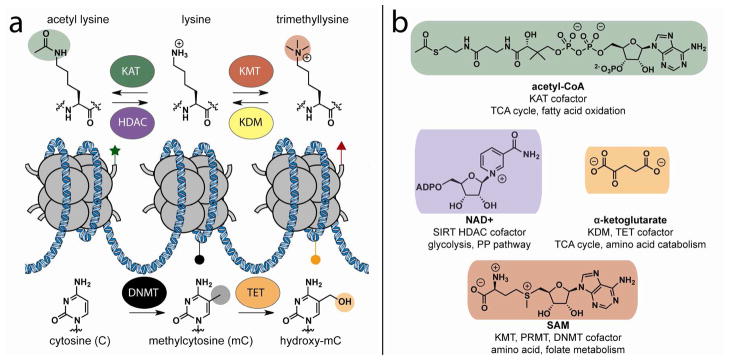
Regulation of genome function by cofactor-dependent enzymes. (a) Chromatin-modifying enzymes modulate the posttranslational modifications of histone amino acids and cytosine methylation state. These modifications can affect the physical accessibility of genomic loci, provide specific binding surfaces for effector proteins, or influence posttranslational modification of neighboring residues. (b) Enzyme cofactors, their associated chromatin modifiers, and examples of metabolic pathways that produce and consume each cofactor. Enzymes are abbreviated according to nomenclature established by Allis et al.117 KAT, lysine acetyltransferase; HDAC, sirtuin histone deacetylase; KMT, lysine methyltransferase; KDM, lysine demethylase; DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; TET, cytosine hydroxylase.
