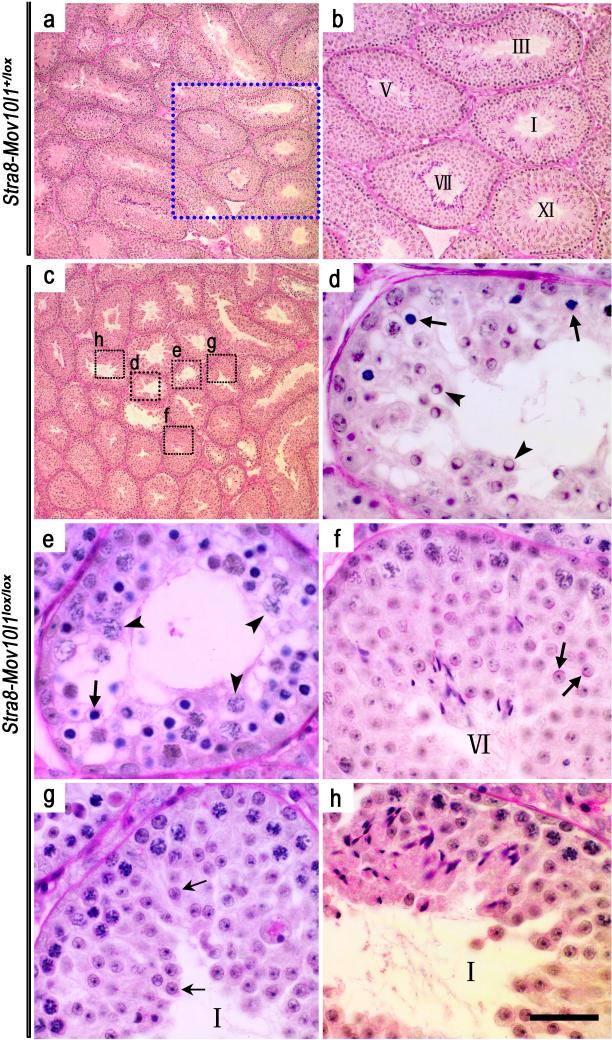
Figure 4. Spermatogenic disruptions in Stra8-iCre; Mov10lox/lox (mosaic) mice.
(a) Normal spermatogenesis in Stra8-iCre; Mov10+/lox testes at postnatal day 60. (b) Enlarged image of the framed area in panel a, showing spermatogenic stages (marked with Roman numerals) of the seminiferous epithelial cycle in Stra8-iCre; Mov10+/lox testes at postnatal day 60. All sections were stained using the periodic acid-Schiff's (PAS) reagent that allows accurate staging based upon the shape of the developing acrosome in spermatids. (c-h) Highly variable spermatogenic disruptions in Stra8-iCre; Mov10lox/lox seminiferous tubules. Panels d-h are magnified images corresponding to the framed area in panel c. (d) Arrows and arrowheads indicate abnormal zygotene spermatocytes and round spermatids, respectively; (e) Arrows and arrowheads demonstrate zygotene-like and pachytene spermatocytes, respectively; Sporadic vacuoles are present, which are generally located in the cytoplasm of Sertoli cells and are indicative of active germ cell depletion. (f) A morphologically normal tubule cross-section containing round spermatids (step 6) (arrows). (g) A seminiferous tubule contains no elongating/elongated spermatids, suggesting a block in the elongation step of spermiogenesis. Arrows indicate the arrested step 4 spermatids. (h) A relatively morphologically normal seminiferous tubule. Scale bar=20μm.