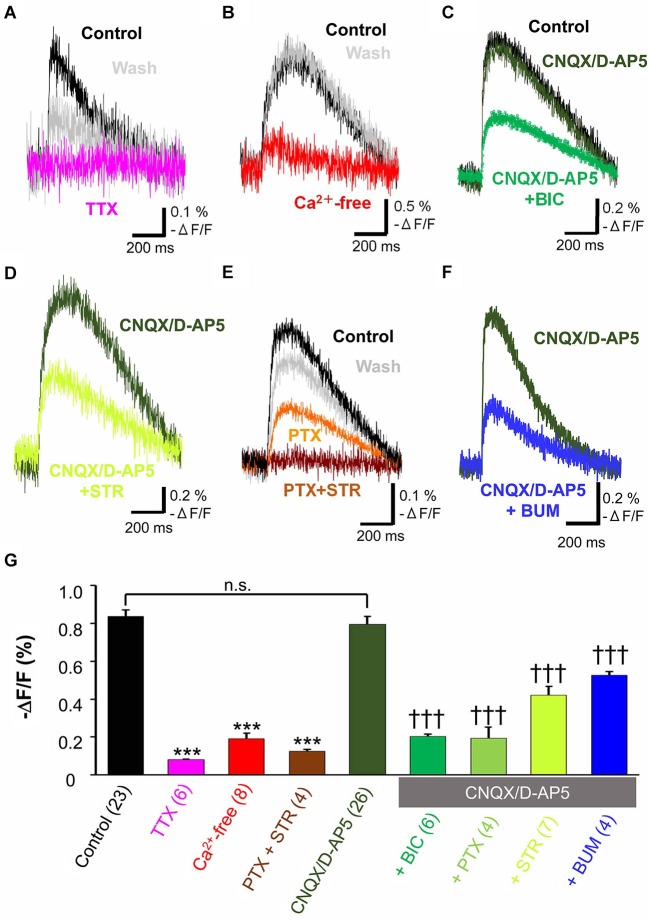
Figure 2.
Pharmacological properties of propagating excitatory optical signals evoked by single electrical stimulation. To normalize responses, changes in fluorescence intensity were divided by the baseline fluorescence intensity (−ΔF/F). (A) Typical traces of voltage sensitive dye signals before and after treatment with TTX (1 µM). Note that the evoked optical signals were completely blocked by TTX (magenta trace) and partially recovered after washing (grey trace). (B) Ca2+-free ACSF largely blocked the evoked signals (red trace). (C) Evoked optical signals were not affected by combined application of CNQX (10 µM) and D-AP5 (50 µM) (dark green trace). By contrast, the residual signal insensitive to glutamate receptor antagonists was inhibited by the GABAA receptor antagonist BIC (50 µM) (green trace). (D) The evoked optical signals were reduced by the glycine receptor antagonist STR (50 µM) (light green trace). (E) The evoked optical signals were attenuated by PTX (50 µM), another GABAA receptor-channel blocker (orange trace). Subsequent addition of 50 µM STR further inhibited it down to baseline intensity (brown trace). The optical signal recovered after washing for 30 min (gray trace). (F) Evoked optical signals insensitive to glutamate receptor antagonists, CNQX and D-AP5, were inhibited by application of a Na+, K+-2Cl− cotransporter inhibitor BUM (20 µM) (blue trace). Electrical stimulation-evoked optical signals were recorded after BUM was present at least for 20 min. (G) Statistical analysis of the pharmacological profile of propagating excitatory optical signals evoked by single electrical stimulation. The spread of excitation was blocked by TTX and in Ca2+-free ACSF. Combined application of PTX and STR also completely abolished the spread of excitation. In contrast, CNQX plus D-AP5 failed to affect the optical signals. Note that the optical signals in the presence of CNQX plus D-AP5 were significantly inhibited by further addition of BIC, PTX or STR (one-way ANOVA, P < 0.001, Post-hoc Tukey test; ***P < 0.001 (vs. control), †††P < 0.001 (vs. CNQX + D-AP5), n.s., not significant.). Addition of BUM also attenuated the spread of excitation. Number of trials in parenthesis. Bars represent the mean ± SEM.