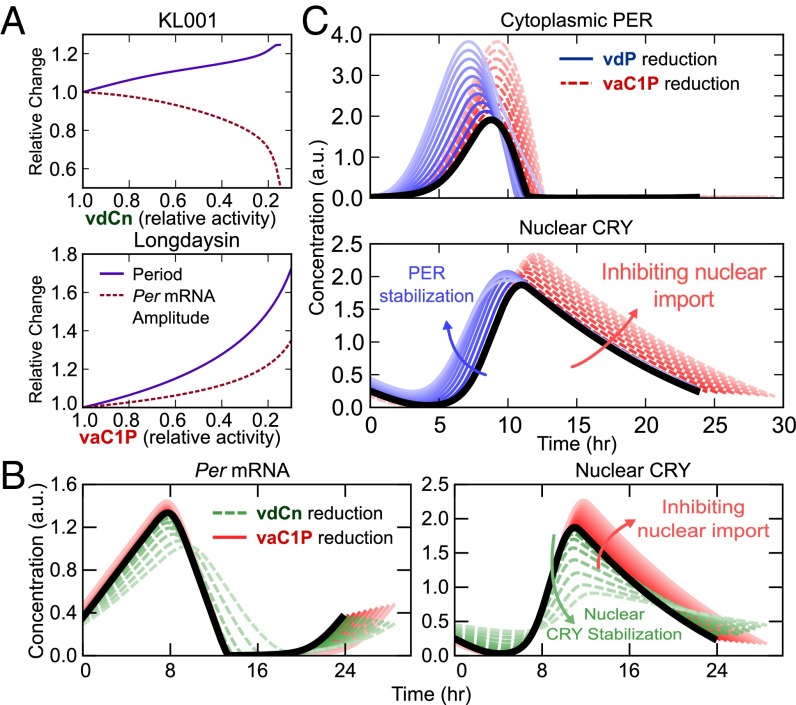
Fig. 4.
Mechanistic insight into the effects of small molecule modulators KL001 and longdaysin. (A) In silico reproductions of the circadian reporter experiments in Fig. 1 B and C, using the predictions identified in Fig. 3. (B) Comparison of the effects of KL001 and longdaysin. Parameter changes were normalized such that the period change was equal for each pair of perturbations (vdCn: 100% → 23%, vaC1P: 100% → 51%). (C) Comparison of two candidate mechanisms for CKI inhibition. Effects of increasing PER stabilization and nuclear import inhibition on the time profiles of cytoplasmic PER (Upper) and nuclear CRY (Lower). Parameter values were selected such that the amplitudes of cytoplasmic PER are equal at each level. Lighter colors indicate stronger perturbations (vdP: 100% → 22%, vaC1P: 100% → 45%); t = 0 is set to the onset of PER accumulation.