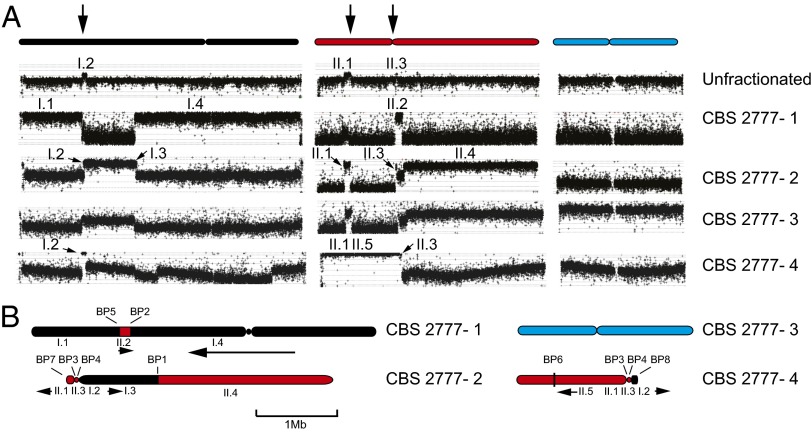
Fig. 1.
Genome organization of S. pombe strain CBS 2777. (A) Sequence content of size- fractionated chromosomes of CBS 2777. Either unfractionated CBS 2777 DNA or DNA from each of the four chromosomes that had been size-fractionated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis was analyzed by CGH using Agilent 4 × 44K ChIP-on-ChIP arrays (G4810A-015424). The results are aligned with respect to the three laboratory strain (972h−) chromosomes listed at the top of the panel and color-coded black, red, and blue, respectively. Chromosome 3 of CBS 2777 is not detectably rearranged, but the DNA used in the CGH was contaminated with CBS 2777 chromosome 2 as predicted, given the small difference in their respective sizes. Segments of the 972h− chromosomes present in the CBS 2777 chromosomes are labeled according to their chromosomal origin using Roman numerals. Segment II.5 extends from II:569,645 to the imr2 left repeat of chromosome II and corresponds to an inversion to which the CGH is insensitive. The three vertical arrows at the top of the figure refer to the three regions of the laboratory strain karyotype that are duplicated around the centromeres of CBS 2777 chromosomes 2 and 4. (B) Arrangement of the sequences identified in A on the CBS 2777 chromosomes. The arrows below the chromosomes indicate whether the respective segment is in the same orientation as in the 972h− genome as drawn at the top or inverted (running right to left). Each of the eight breakpoints (BP 1–8) defining the CBS 2777 karyotype is indicated.