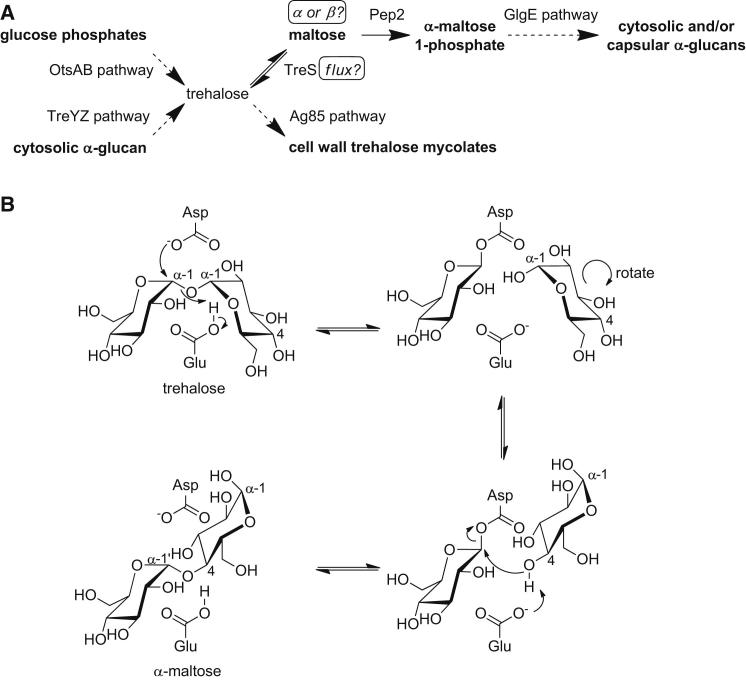
Figure 1.
Metabolism of Trehalose in Mycobacteria and Proposed Mechanism of TreS
(A) All known metabolic pathways associated with trehalose in mycobacteria are shown, except for its hydrolysis by trehalase to form glucose as a carbon source for growth (Carroll et al., 2007). The questions addressed by this work are indicated in boxes.
(B) Proposed catalytic mechanism of TreS with the most likely relative orientations of the glucose rings of trehalose and maltose. Hydrolysis would be expected to occur when water attacks the glucosyl-enzyme intermediate, generating a second glucose molecule with an α anomeric configuration.