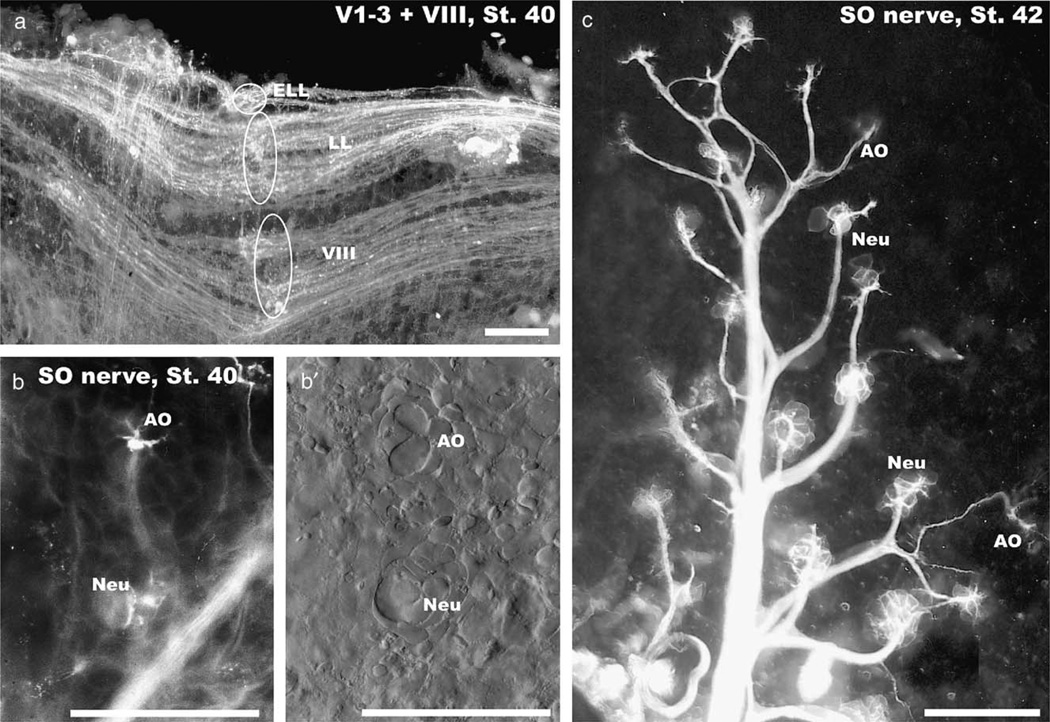
Fig. 4.
At stage 40 all octavolateral afferents extend in an adult pattern along the alar plate (a) and different organs can be identified in the skin (b, c). Separate roots for inner ear (VIII), lateral line (LL) and electroreceptive ampullary organ afferents (ELL) at rhombomere 4 are indicated (ovals and circle in a). Ampullary organs (AO) and neuromasts (Neu) show differences in the pattern of innervation (b, c) and the distribution of cells as revealed with differential interference microscopy (b′). Note that ampullary organs (AO) are always further away from the main trunk of the superficial ophthalmic nerve (SO) than the neuromasts (Neu). Bars indicate 100 µm in all images.