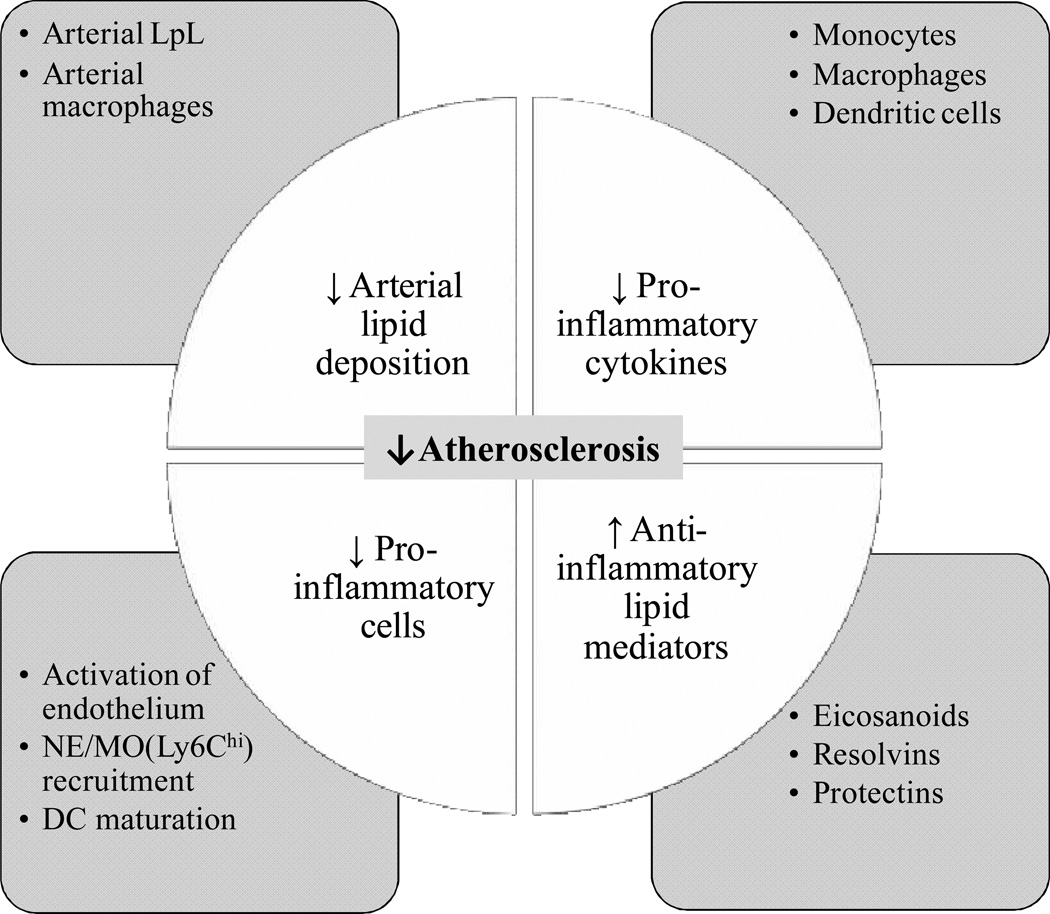
Figure 1. Summary of potential “beneficial effects” of n-3 FA in atherosclerosis.
n-3 FA modulate atherosclerosis by affecting uptake and binding of LDL to the arterial wall. This is associated with reduced arterial LpL and macrophage levels. n-3 FA are protective against inflammation in the arterial wall by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in monocytes (MO), macrophages or dendritic cells (DC) and decreasing the recruitment of inflammatory leukocytes to the arterial wall, including neutrophils (NE) and MO. Lastly, n-3 FA and n-3-derived eicosanoids, resolvins and protectins are potential anti-inflammatory lipid mediators in atherosclerosis. Specific examples of pathways related to each area are shown in the square boxes.