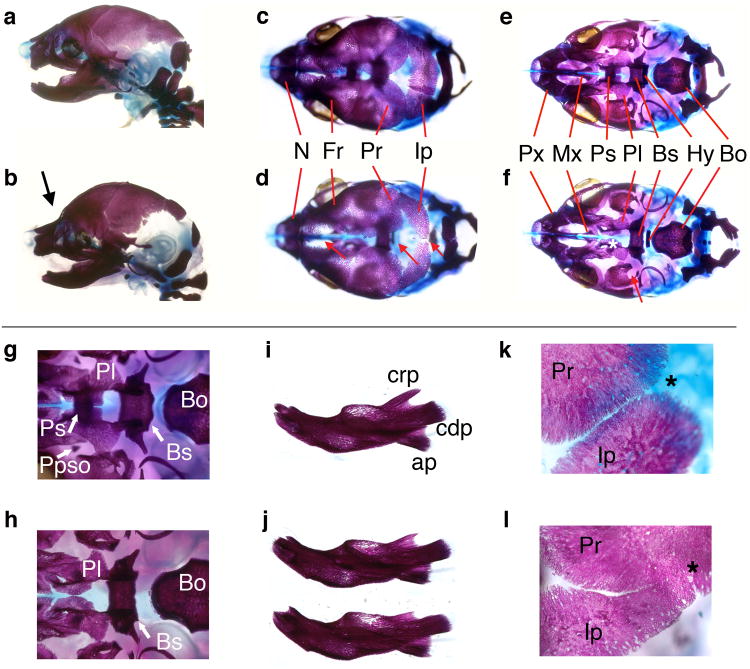
Figure 2.
Craniofacial skeletal abnormalities in Ptch1DL homozygous mutants.
E18.5 control (a, c, e, g, i, k) and Ptch1DL mutant skulls (b, d, f, h, j, l) shown in lateral (a, b), dorsal (c, d) and ventral views with mandibles removed (e-h). (g) and (h) show detail of cranial base with hyoid bone removed. (Note that the pila postopitca (Ppso), which forms a component of the orbitosphenoid, was occasionally present in the mutants. It can also be absent in control embryos at this stage). (i, j) lateral views of control dentary bone (i) and dentary bones from two separate Ptch1DL mutants (j). (k, l) show detail of lambdoid suture between parietal and interparietal bones. Midline is to left and lateral to right. Asterisk shows expected junction between bones.
Key. (b) Abnormal flexure at skull and nasal juncture is shown by a black arrow. (d) Red arrows demonstrate delayed or abnormal development of the bones of the cranial vault in the midline in Ptch1DL mutants. (f) White asterisk highlights the absence of the presphenoid bone and the underdevelopment of the palatal shelves, red arrow shows the abnormal morphology of the alisphenoid bone in Ptch1DL mutants. Bo, basioccipital; Bs, basisphenoid; cdp, condylar process; crp, coronoid process; Fr, frontal bone; Hy, hyoid; Ip, interparietal bone; Mx, palatine process of the maxilla; N, nasal bone; Pl, palatine; Ppso, pila postoptica; Pr, parietal bone; Ps, presphenoid; Px, premaxilla.