Figure 4.
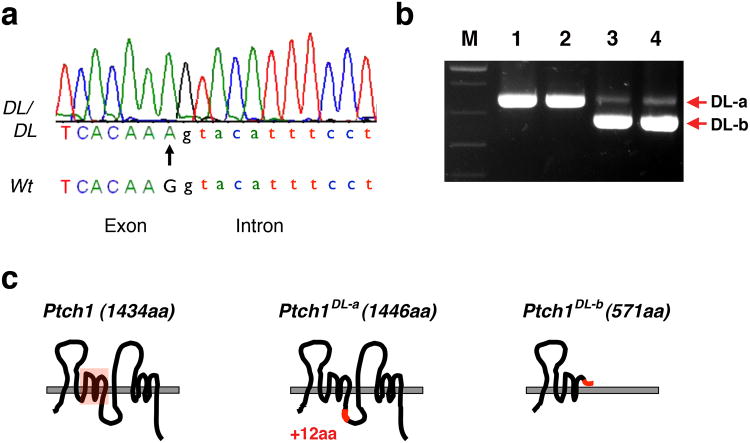
Ptch1DL harbors a point mutation in Ptch1. (a) Chromatograph sequencing result for Ptch1DL mutant showing Ptch1 genomic sequences at the junction of exon 13 and intron 13. The G to A point mutation in the Ptch1DL mutant is labeled with an arrow. (b) RT-PCR results for wild-type (lanes 1 and 2) and Ptch1DL mutant embryos (lanes 3 and 4) obtained using Ptch1 primers Pt2F and Pt2R. “M” = markers. (c) Graphic representation of wild-type Ptch1 protein and two putative Ptch1 proteins based on their mRNA sequences in Ptch1DL mutant embryos. The sterol sensing domain is shown by the red box in the wild-type protein. The DL-a form changes the normal sequence from DIFCC FTSPC VSRVI to DIFCC FTKYI SWCLG PVFFG PCVSR VI i.e. the addition of 36 nucleotides, with a new in-frame splice at a GGGT donor sequence, the change of S to K followed by the addition of 12 new amino acids. The DL-b form changes the normal sequence from FSLQA AVVVV FN to FSLQP LCQQG DSS* as exon 13, which has the mutated splice donor sequence, is skipped. The resulting splice from exon 12 to 14 is out of frame and creates a premature stop codon after 9 amino acids.