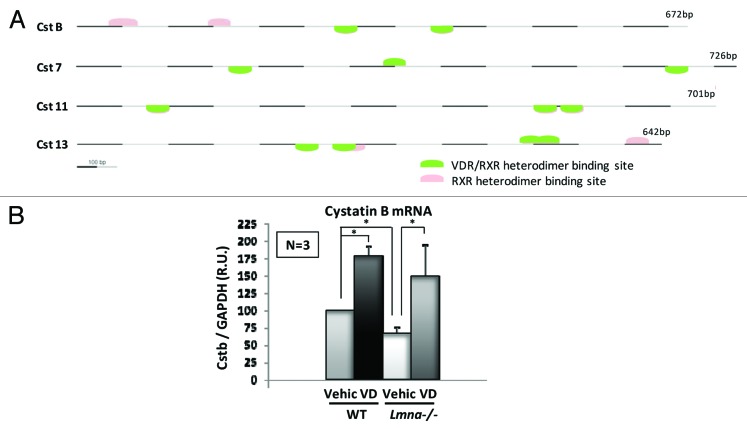
Figure 2. Vitamin D-dependent inhibition of CTSL activity may be mediated by cystatins. (A) Promoter analysis for vitamin D responding elements (VDREs) in the 13 cystatins encoded in the mouse genome resulted in four candidate genes containing at least two RXR/VDR heterodimer binding sites. (B) qRT-PCR experiments show that cystatin B expression is downregulated in lamins-deficient cells. Treatment with vitamin D 10−7 M for 48 h increases cystatin B expression in both wild-type and Lmna-KO MEFs. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. N, the number of independent experiments; *, p value of statistical significance (P ≤ 0.05); R. U., relative units (normalization to GAPDH).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.