Figure 2. Defects in the cellular composition and arrangement of asund93 egg chambers.
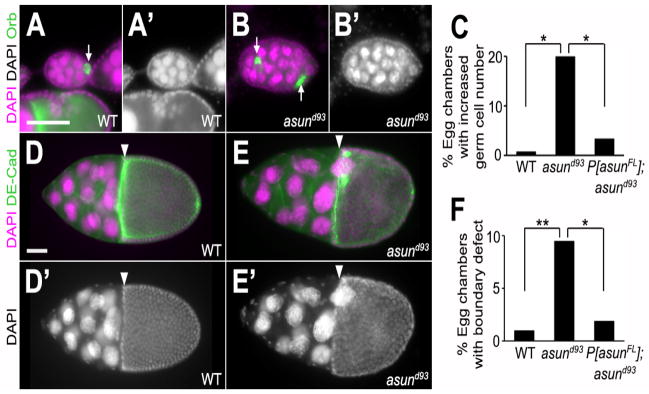
(AB′) Stage 5 egg chambers stained for DNA (magenta; grayscale in A′ and B′) and Orb (green; oocyte marker) from wild-type and asund93 ovaries (dorsal, top; anterior, left). Wild-type egg chambers (A,A′) contain 15 polyploid nurse cells and 1 haploid oocyte. asund93 ovaries occasionally contain compound/fused egg chambers (B,B′). White arrows point to oocytes. (C) Quantification of fused egg chamber defect in ovaries of indicated genotypes (>250 chambers scored per genotype). Asterisks, p<0.0001. (D–E′) Stage 10 egg chambers stained for DNA (magenta; grayscale in D′ and E′) and DE-cadherin (green; cell membrane marker) from wild-type and asund93 ovaries (dorsal, top; anterior, left). There is a clear boundary (white arrowhead) between the nurse cells and the oocyte in stage 10 wild-type egg chambers (D,D′). Nurse cells occasionally extend past this boundary in asund93 stage 10 egg chambers (E,E′). (F) Quantification of nurse cell-oocyte boundary defect in ovaries of indicated genotypes (>200 chambers scored per genotype). Single asterisk, p=0.0006; double asterisk, p<0.0001. Scale bars, 50 μm.
